Comparison of three non-insulin-based insulin resistance indexes in predicting the presence and severity of coronary artery disease
- PMID: 35966520
- PMCID: PMC9374164
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.918359
Comparison of three non-insulin-based insulin resistance indexes in predicting the presence and severity of coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance (IR) has emerged as a risk factor for coronary heart disease (CAD), but there is currently insufficient data on the association of non-insulin-based IR indexes [triglyceride (TG)/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio, triglyceride and glucose (TyG) index, and metabolic score for IR (METS-IR)] with the presence and severity of CAD. Thus, the present study aimed to examine the relationship between these three non-insulin-based IR indexes and CAD, as well as to further compare the predictive values of each index.
Materials and methods: In total, 802 consecutive patients who underwent coronary angiography for suspected CAD from January 2016 to April 2017 were included in this study and were divided into the control group (n = 149) and CAD group (n = 653) according to the angiography results. The triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio, triglyceride and glucose index (TyG index), and METS-IR were calculated according to the corresponding formulas. The severity of CAD was evaluated using the Gensini score (GS). The relationship of the TG/HDL-C ratio, TyG index, and METS-IR with CAD was analyzed, and the predictive values of the indexes were compared.
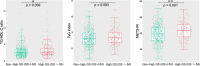
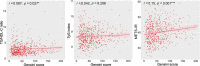
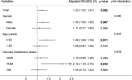
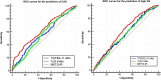
Results: The TG/HDL-C ratio, TyG index, and METS-IR in the CAD group were significantly higher than those in the control group. The TG/HDL-C ratio and METS-IR in the high GS group were significantly higher than those in the non-high GS group. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the TG/HDL-C ratio and METS-IR were independent predictors for the presence of CAD {adjusted odds ratio (OR) [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 1.32 (1.02-1.70) and 1.65 (1.32-2.05), respectively}, whereas only the METS-IR was an independent predictor of the severity of CAD [adjusted OR (95% CI): 1.22 (1.02-1.47)]. Further subgroup analysis indicated that statistical significance was observed only among men, younger patients (≤ 60), and patients with prediabetes mellitus (PDM). Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis showed that the METS-IR had the highest predictive value for the prediction of both the presence and severity of CAD.
Conclusion: The TG/HDL-C ratio, TyG index, and METS-IR are valuable predictors of the presence and severity of CAD, and the METS-IR has the highest predictive value among the three non-insulin-based IR indexes.
Keywords: Gensini score; coronary artery disease; metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR); triglyceride and glucose index (TyG index); triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Cui, Li, Zhang, Liu, Liu, Zhang, Zheng and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-insulin-based insulin resistance indexes in predicting severity for coronary artery disease.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022 Dec 17;14(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00967-x. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 36528713 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index as a superior marker of insulin resistance for predicting long-term major adverse cardiovascular events following coronary artery bypass grafting in China.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 22;15(1):6450. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87967-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39987346 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index, triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio, and metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) associated with periodontitis in Korean adults.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022 Sep 12;13:20406223221122671. doi: 10.1177/20406223221122671. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022. PMID: 36120508 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of risk, severity, and prognosis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jul 6;22(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01906-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37415168 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Triglyceride-Glucose Index for Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Dec 2;8:774781. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.774781. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34926622 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cross-sectional comparison of the association between three different insulin resistance surrogates and frailty: NHANES 1999-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 23;15:1439326. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1439326. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39247923 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Different Insulin Resistance Indices and Heart Failure in US Adults With Diabetes Mellitus.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2024 Nov;29(6):e70035. doi: 10.1111/anec.70035. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2024. PMID: 39545717 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) among health check-up population in Japan: A retrospective cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 16;13:1027262. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1027262. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36589854 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic score for insulin resistance predicts major adverse cardiovascular event in premature coronary artery disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 1;16(7):6364-6383. doi: 10.18632/aging.205710. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38568104 Free PMC article.
-
Association between metabolic score for insulin resistance and lower limb pain among the elderly: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 24;16:1530067. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1530067. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40630098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. (2020) 141:e139–596. - PubMed
-
- Taube A, Schlich R, Sell H, Eckardt K, Eckel J. Inflammation and metabolic dysfunction: links to cardiovascular diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2012) 302:H2148–65. - PubMed
-
- Beverly JK, Budoff MJ. Atherosclerosis: pathophysiology of insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and inflammation. J Diabetes. (2020) 12:102–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

