Online searches for SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists correlate with prescription rates in the United States: An infodemiological study
- PMID: 35966558
- PMCID: PMC9372305
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.936651
Online searches for SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists correlate with prescription rates in the United States: An infodemiological study
Abstract
Several clinical trials have demonstrated that many SGLT-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with Type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Recent reports indicate an underutilization of new cardiometabolic drugs, including SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA. We aimed to evaluate the use of online search volumes to reflect United States prescription rates. A repeated cross-sectional analysis of Google search volumes and corresponding data from the IQVIA National Prescription Audit (NPA) of pharmacy dispensing of newly prescribed drugs was performed. Monthly data for online searches and prescription between January 1, 2016 and December 31, 2021 were collected for selected SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA. Prescription data for drugs classes (SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA) and individual drugs were calculated as the total of queried data for branded drug names. Trends were analyzed for visual and quantitative correlation as well as predictive patterns. Overall, online searches increased by 157.6% (95% CI: 142.2-173.1%) and 295.2% (95% CI: 257.7-332.6%) for SGLT2i and GLP-1RA between 2016 and 2021. Prescription rates raised by 114.6% (95% CI: 110.8-118.4%) and 221.0% (95% CI: 212.1-229.9%) for SGLT2i and GLP-1RA for this period. Correlation coefficients (range 0.86-0.99) were strongest for drugs with growing number of prescriptions, for example dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, ertugliflozin, dulaglutide, and semaglutide. Online searches might represent an additional tool to monitor the utilization trends of cardiometabolic drugs. Associations were strongest for drugs with reported cardioprotective effect. Thus, trends in online searches complement conventionally acquired data to reflect and forecast prescription trends of cardiometabolic drugs.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonist; Google trends; SGLT 2 inhibitors; cardiometabolic medicine; national prescription audit.
Copyright © 2022 Dzaye, Berning, Razavi, Adhikari, Jha, Nasir, Ayers, Mortensen and Blaha.
Conflict of interest statement
MB reports grants from the National Institutes of Health, US Food and Drug Administration, American Heart Association, Bayer, and Novo Nordisk; Advisory Boards with Amgen, Sanofi, Regeneron, Novartis, Bayer, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Inozye, 89Bio, and Kaleido outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

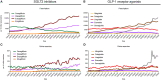
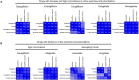
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National Diabetes Statistics Report Website. (2022). Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html (accessed May 1, 2022).
-
- Kristensen SL, Rorth R, Jhund PS, Docherty KF, Sattar N, Preiss D, et al. . Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2019) 7:776–85. 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30249-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Bonaca MP, et al. . SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. (2019) 393:31–9. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

