Emergently Alteration of Procedural Strategy During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement to Prevent Coronary Occlusion: A Case Report
- PMID: 35966563
- PMCID: PMC9363569
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.931595
Emergently Alteration of Procedural Strategy During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement to Prevent Coronary Occlusion: A Case Report
Abstract
Background: Coronary occlusion is an uncommon but fatal complication of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) with a poor prognosis.
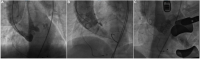
Case presentation: A patient with symptomatic severe bicuspid aortic valve stenosis was admitted to a high-volume center specializing in transfemoral TAVR with self-expanding valves. No anatomical risk factors of coronary occlusion were identified on pre-procedural computed tomography analysis. The patient was scheduled for a transfemoral TAVR with a self-expanding valve. Balloon pre-dilatation prior to prosthesis implantation was routinely used for assessing the supra-annular structure and assessing the risk of coronary occlusion. Immediately after the tubular balloon inflation, fluoroscopy revealed that the right coronary artery was not visible, and the flow in the left coronary artery was reduced. The patient would be at high-risk of coronary occlusion if a long stent self-expanding valve was implanted. Therefore, our heart team decided to suspend the ongoing procedure. A transapical TAVR with a 23 mm J-valve was performed 3 days later. The prosthesis was deployed at a proper position without blocking the coronary ostia and the final fluoroscopy showed normal flow in bilateral coronary arteries with the same filling as preoperatively.
Discussion: Our successful case highlights the importance of a comprehensive assessment of coronary risk and a thorough understanding of the TAVR procedure for the heart team. A short-stent prosthesis is feasible for patients at high risk of coronary occlusion. Most importantly TAVR should be called off even if the catheter has been introduced when an extremely high risk of coronary obstruction is identified during the procedure and no solution can be found.
Keywords: aortic valve stenosis; emergent; pre-dilatation; procedural strategy; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
Copyright © 2022 Dai, Zhou, Fan, Wang, Yidilisi, Zhu, Jiang, Li, Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Otto CM, Nishimura RA, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP, III, Gentile F, et al. 2020 ACC/AHA guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: executive summary: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 77:450–500. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.035 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro HB, Webb JG, Makkar RR, Cohen MG, Kapadia SR, Kodali S, et al. Predictive factors, management, and clinical outcomes of coronary obstruction following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: insights from a large multicenter registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 62:1552–62. 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.040 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

