A novel of new class II bacteriocin from Bacillus velezensis HN-Q-8 and its antibacterial activity on Streptomyces scabies
- PMID: 35966655
- PMCID: PMC9372549
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.943232
A novel of new class II bacteriocin from Bacillus velezensis HN-Q-8 and its antibacterial activity on Streptomyces scabies
Abstract
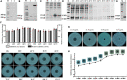
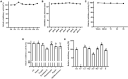
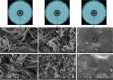
Potato common scab is a main soil-borne disease of potato that can significantly reduce its quality. At present, it is still a challenge to control potato common scab in the field. To address this problem, the 972 family lactococcin (Lcn972) was screened from Bacillus velezensis HN-Q-8 in this study, and an Escherichia coli overexpression system was used to obtain Lcn972, which showed a significant inhibitory effect on Streptomyces scabies, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 10.58 μg/mL. The stability test showed that Lcn972 is stable against UV radiation and high temperature. In addition, long-term storage at room temperature and 4°C had limited effects on its activity level. The antibacterial activity of Lcn972 was enhanced by Cu2+ and Ca2+, but decreased by protease K. The protein was completely inactivated by Fe2+. Cell membrane staining showed that Lcn972 damaged the cell membrane integrity of S. scabies. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observations revealed that the hyphae of S. scabies treated with Lcn972 were deformed and adhered, the cell membrane was incomplete, the cytoplasm distribution was uneven, and the cell appeared hollow inside, which led to the death of S. scabies. In conclusion, we used bacteriocin for controlling potato common scab for the first time in this study, and it provides theoretical support for the further application of bacteriocin in the control of plant diseases.
Keywords: Bacillus; Lcn972; Streptomyces scabies; potato; potato common scab.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Zhou, Bai, Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Wu, Zhu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Arevalos-Sánchez M., Regalado C., Martin S. E., Domínguez-Domínguez J., García-Almendárez B. E. (2012). Effect of neutral electrolyzed water and nisin on Listeria monocytogenes biofilms, and on listeriolysin O activity. Food Control 24 116–122. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.09.012 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

