Potential roles of gut microbial tryptophan metabolites in the complex pathogenesis of acne vulgaris
- PMID: 35966699
- PMCID: PMC9363916
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.942027
Potential roles of gut microbial tryptophan metabolites in the complex pathogenesis of acne vulgaris
Abstract
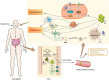
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disease in which the influence of gut microbiota has been implicated but without clarification of mechanisms. Gut microbiota may exert such an influence via metabolites, particularly those of tryptophan. End metabolites of tryptophan activate receptors, including aryl hydrocarbon, G protein-coupled, and pregnane X receptors to stabilize the immune microenvironment and intestinal mucosal homeostasis. Any impact on the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris remains unclear. The current review collates recent advances concerning potential roles of tryptophan metabolism in mediating skin inflammation, follicular sebaceous gland function and intestinal permeability, all of which influence the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. The aim was to improve understanding of the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris and to expose therapeutic opportunities.
Keywords: acne vulgaris; aryl hydrocarbon receptors; gut microbiota (GM); metabolite; tryptophan.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Liu, Hao, Chen, Yang, Xiong and Deng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abel J., Haarmann-Stemmann T. (2010). An introduction to the molecular basics of aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology. Biol. Chem. 391 1235–1248. - PubMed
-
- Abron J. D., Singh N. P., Mishra M. K., Price R. L., Nagarkatti M., Nagarkatti P. S., et al. (2018). An endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand, ITE, induces regulatory T cells and ameliorates experimental colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 315 G220–G230. 10.1152/ajpgi.00413.2017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

