Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation with Average Volume-Assured Pressure Support versus BiPAP S/T in De Novo Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
- PMID: 35966802
- PMCID: PMC9365614
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4333345
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation with Average Volume-Assured Pressure Support versus BiPAP S/T in De Novo Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
Abstract
Background: Bilevel positive airway pressure in spontaneous/time and average volume-assured pressure support (BiPAP·S/T-AVAPS) could maintain an adequate tidal volume by reducing the patient's inspiratory effort; however, this ventilatory strategy has not been compared with other ventilatory modes, especially the conventional BiPAP S/T mode, when noninvasive mechanical ventilation (NIMV) is used. The primary objective of this study was to determine the rate of success and failure of the use of BiPAP·S/T-AVAPS versus BiPAP·S/T alone in patients with mild-to-moderate "de novo" hypoxemic respiratory failure.
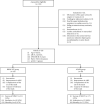
Methods: This was a matched-cohort study. Subjects with mild-to-moderate de novo hypoxemic respiratory failure were divided into two groups according to the ventilatory strategy used. The subjects in the BiPAP·S/T group were paired with those in the BiPAP·S/T-AVAPS group.
Results: A total of 58 subjects were studied. Twenty-nine subjects in the BiPAP·S/T group were paired with 29 subjects in the BiPAP·S/T-AVAPS group. Twenty patients (34.5%) presented with "failure of NIMV," while 38 (65.5%) patients did not. In addition, 13 (22.4%) patients died, while 45 (77.6%) recovered. No differences were found in the percentage of intubation (P=0.44) and mortality (P=0.1).
Conclusion: The BiPAP S/T-AVAPS ventilator mode was not superior to the BiPAP·S/T mode. A high mortality rate was observed in patients with NIMV failure in both modes. This trial is registered with https://doi.org/10.1186/ISRCTN17904857.
Copyright © 2022 Killen H. Briones-Claudett et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yarrarapu S. N. S., Saunders H., Sanghavi D. Average Volume-Assured Pressure Support . Tampa, FL, USA: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources