Sulfonylureas or biguanides is associated with a lower risk of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with diabetes: A nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 35966856
- PMCID: PMC9363881
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.934184
Sulfonylureas or biguanides is associated with a lower risk of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with diabetes: A nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with immune dysregulation, while sulfonylureas or biguanides have been linked to anti-inflammatory mechanisms. In this study, we aimed to examine the occurrence rate of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) among DM patients and its incidence rate between different treatments.
Methods: This cohort study used the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database between 1997 and 2013 to evaluate the primary outcomes of the preventive role of sulfonylureas or biguanides in the development of RA. We used the Chi-square test for categorical variables and Cox proportional hazard regression and log-rank test to explore the time for development of RA in DM patients. Logistic regression was adopted to estimate the odds ratio of RA in different dosages of medication exposure.
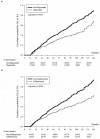
Results: Our cohort study included 94,141 DM cases. The risk of RA development of non-sulfonylureas/biguanides users among the DM group in each analysis was set as the reference, and the adjusted hazard ratio of RA in DM patients who were using sulfonylureas or biguanides was 0.73 (95% confidence interval 0.60-0.90). Within 1 year before the index date, compared with no-biguanides users, patients with more than 180 days of prescription of biguanides had a significantly lower RA risk. Similarly, the significantly lower risk of RA was still observed in DM patients who had more than 365 days of prescription of sulfonylurea within 2 or 3 years before the index date of first RA visit (all p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Our data suggest that sulfonylureas or biguanides are associated with a lower rate of RA development in patients with DM; the effect of biguanides appeared more rapid than that of sulfonylureas, but the sulfonylureas might have a longer effect on lowering RA development incidence.
Keywords: biguanides; diabetes; incidence rate; rheumatoid arthritis; sulfonylureas.
Copyright © 2022 Su, Huang, Chu and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased risk of gastrointestinal malignancy in patients with diabetes mellitus and correlations with anti-diabetes drugs: a nationwide population-based study in Taiwan.Intern Med. 2013;52(9):939-46. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.52.8276. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23648711
-
Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020 Sep;72(9):1248-1256. doi: 10.1002/acr.24343. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 32754989
-
Periodontitis exposure within one year before anti-diabetic treatment and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis in diabetes mellitus patients: a population-based cohort study.Rev Bras Reumatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;54(2):124-30. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2014. PMID: 24878859 English, Portuguese.
-
Antidiabetic medications in overdose: a comparison of the inquiries made to a regional poisons unit regarding original sulfonylureas, biguanides and insulin.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Feb;44(2):51-6. doi: 10.5414/cpp44051. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16502763
-
Is diabetes mellitus associated with clinical outcomes in aging males treated with transurethral resection of prostate for bladder outlet obstruction: implications from Taiwan Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study.Clin Interv Aging. 2017 Mar 16;12:535-541. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S126207. eCollection 2017. Clin Interv Aging. 2017. PMID: 28356725 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association Between T2DM, TyG Index, Multiple Sclerosis, and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights into Potential Mechanisms.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Sep;62(9):11297-11316. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04961-y. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40279037
-
Insulin Sensitivity Controls Activity of Pathogenic CD4+ T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2024 Dec 22;13(24):2124. doi: 10.3390/cells13242124. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39768214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma J, Khalidi N, Wierzbicki O, Alqutami A, Ioannidis G, Pagnoux C. Impact of diabetes, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker use, and statin use on presentation and outcomes in patients with giant cell arteritis. Int J Rheum Dis. (2020) 23:1233–9. 10.1111/1756-185X.13914 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lai YR, Huang CC, Chiu WC, Liu RT, Tsai NW, Wang HC, et al. . HbA1C variability is strongly associated with the severity of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes after longer diabetes duration. Front Neurosci. (2019) 13:458. 10.3389/fnins.2019.00458 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

