Protease-activated receptor-2: Role in asthma pathogenesis and utility as a biomarker of disease severity
- PMID: 35966869
- PMCID: PMC9372307
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.954990
Protease-activated receptor-2: Role in asthma pathogenesis and utility as a biomarker of disease severity
Abstract
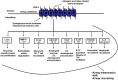
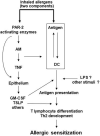
PAR2, a receptor activated by serine proteases, has primarily pro-inflammatory roles in the airways and may play a role in asthma pathogenesis. PAR2 exerts its effects in the lungs through activation of a variety of airway cells, but also activation of circulating immune cells. There is evidence that PAR2 expression increases in asthma and other inflammatory diseases, although the regulation of PAR2 expression is not fully understood. Here we review the available literature on the potential role of PAR2 in asthma pathogenesis and propose a model of PAR2-mediated development of allergic sensitization. We also propose, based on our previous work, that PAR2 expression on peripheral blood monocyte subsets has the potential to serve as a biomarker of asthma severity and/or control.
Keywords: PAR-2; allergic disease; asthma; biomarker; severity.
Copyright © 2022 Gandhi, Shrestha Palikhe and Vliagoftis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

