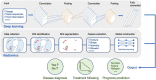
The Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Drug Resistance Prediction of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- PMID: 35966878
- PMCID: PMC9366014
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.935080
The Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Drug Resistance Prediction of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Abstract
With the increasing incidence and mortality of pulmonary tuberculosis, in addition to tough and controversial disease management, time-wasting and resource-limited conventional approaches to the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of tuberculosis are still awkward issues, especially in countries with high tuberculosis burden and backwardness. In the meantime, the climbing proportion of drug-resistant tuberculosis poses a significant hazard to public health. Thus, auxiliary diagnostic tools with higher efficiency and accuracy are urgently required. Artificial intelligence (AI), which is not new but has recently grown in popularity, provides researchers with opportunities and technical underpinnings to develop novel, precise, rapid, and automated implements for pulmonary tuberculosis care, including but not limited to tuberculosis detection. In this review, we aimed to introduce representative AI methods, focusing on deep learning and radiomics, followed by definite descriptions of the state-of-the-art AI models developed using medical images and genetic data to detect pulmonary tuberculosis, distinguish the infection from other pulmonary diseases, and identify drug resistance of tuberculosis, with the purpose of assisting physicians in deciding the appropriate therapeutic schedule in the early stage of the disease. We also enumerated the challenges in maximizing the impact of AI in this field such as generalization and clinical utility of the deep learning models.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; machine learning; pulmonary tuberculosis; radiomics.
Copyright © 2022 Liang, Ma, Wang, Shao, Li, Deng, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence in Thyroid Field-A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 22;13(19):4740. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194740. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence Assisting the Early Detection of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis From Chest X-Rays: A Population-Based Study.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 8;9:874475. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.874475. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35463963 Free PMC article.
-
AI applications to medical images: From machine learning to deep learning.Phys Med. 2021 Mar;83:9-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Phys Med. 2021. PMID: 33662856 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence for Antimicrobial Resistance Prediction: Challenges and Opportunities towards Practical Implementation.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;12(3):523. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030523. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Application of Machine Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis, Prediction, and Classification of Cardiovascular Diseases.Circ J. 2021 Aug 25;85(9):1416-1425. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-20-1121. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Circ J. 2021. PMID: 33883384 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of drug resistance in pulmonary tuberculosis patients with positive sputum tuberculosis culture in Northeast China.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 25;14:1263726. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1263726. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37818197 Free PMC article.
-
How could emerging nanomedicine-based tuberculosis treatments outperform conventional approaches?Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Apr;20(7):645-647. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2458447. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39877965 No abstract available.
-
Advances in computational frameworks in the fight against TB: The way forward.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 3;14:1152915. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1152915. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37077815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Model for predicting drug resistance based on the clinical profile of tuberculosis patients using machine learning techniques.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Oct 14;10:e2246. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2246. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39650511 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing diagnosis of pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on CT: a systematic review of imaging analysis through deep learning.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1510026. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1510026. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39845042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health O. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2021).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources