Precision medicine based on the phenotypic differences in peripheral T helper cells in patients with psoriatic arthritis: One year follow-up outcomes
- PMID: 35966881
- PMCID: PMC9363692
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.934937
Precision medicine based on the phenotypic differences in peripheral T helper cells in patients with psoriatic arthritis: One year follow-up outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: We validated the one-year effectiveness of strategic treatment with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) based on peripheral T-lymphocytic phenotyping and explored the impact of treatment on T helper lymphocytic phenotypes.
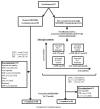
Methods: Ninety-seven patients were registered in this study. One-year treatment response was compared between the two groups: the strategic bDMARDs treatment group (n = 41), in which bDMARDs were selected based on peripheral blood lymphocyte analysis, and the standard bDMARDs treatment group (n = 56), in which the patients underwent no strategic selection of bDMARDs and phenotyping. Changes in helper T lymphocytic phenotypes were evaluated after 1-year post-treatment.
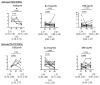
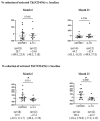
Results: In the standard bDMARDs treatment group, 23 patients (42.6%) achieved disease activity in psoriatic arthritis (DAPSA)-remission (REM), and 23 of 46 (50.0%) achieved PASI 90. In the strategic bDMARDs treatment group, 22 (53.7%) achieved DAPSA-REM, and 26 of 35 (74.2%) achieved PASI90. The rate of achieving minimal disease activity (MDA) and DAPSA-REM at month 6, DAPSA-low disease activity (LDA) at months 6 and 12, and PASI 90 at month 12 were significantly higher in the strategic bDMARDs treatment group. After treatment with ustekinumab, the proportion of aTh1/CD4 (%) significantly decreased. The percent reduction in activated Th17 cells was significantly higher in IL-17-i cells than in UST/TNF-i cells.
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrate the 1-year effectiveness of precision medicine based on peripheral T-lymphocytic phenotyping in terms of DAPSA and MDA. Analysis of data from real-world clinical practice showed that the impact on the immune system varied among bDMARDs. However, because psoriatic arthritis has very high heterogeneity, it may be necessary to conduct studies with a larger sample size, perhaps drawing samples from multiple institutions.
Keywords: biological DMARDs; peripheral T lymphocyte phenotyping; precision medicine; psoriatic arthritis; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Miyagawa, Nakayamada, Ueno, Miyazaki, Ohkubo, Inoue, Kubo and Tanaka.
Conflict of interest statement
YT has received speaking fees and/or honoraria from Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Novartis, YL Biologics, Bristol-Myers, Eisai, Chugai, Abbvie, Astellas, Pfizer, Sanofi, Asahi-kasei, GSK, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Gilead, and Janssen; research grants from Abbvie, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Chugai, Asahi-Kasei, Eisai, Takeda, Daiichi-Sankyo; and consultant fees from Eli Lilly, Daiichi-Sankyo, Taisho, Ayumi, Sanofi, GSK, and Abbvie. SN has received consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from Bristol-Myers, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Astellas, Asahi-kasei, Sanofi, Abbvie, Eisai, Chugai, Gilead, and Boehringer Ingelheim, and has received research grants from Mitsubishi-Tanabe. YM has received consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from Eli Lilly, and has received research grants from GlaxoSmithKline. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Precision medicine using different biological DMARDs based on characteristic phenotypes of peripheral T helper cells in psoriatic arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Feb 1;58(2):336-344. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key069. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 29618121 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of disease activity index for psoriatic arthritis (DAPSA) and minimal disease activity (MDA) targets for patients with psoriatic arthritis: A post hoc analysis of data from phase 3 tofacitinib studies.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023 Feb;58:152134. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152134. Epub 2022 Nov 13. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023. PMID: 36476498 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of serum interleukin-22 as a biomarker for the differential use of molecular targeted drugs in psoriatic arthritis: a retrospective study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Apr 15;24(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02771-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35428323 Free PMC article.
-
Remission and low disease activity in psoriatic arthritis publications: a systematic literature review with meta-analysis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Aug 1;59(8):1818-1825. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa030. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 32118267
-
Infection risk in patients undergoing treatment for inflammatory arthritis: non-biologics versus biologics.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020 Feb;16(2):207-228. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1705785. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31852268 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between life's simple 7 (LS7) and arthritis: the mediating role of body fat percentage (BFP).Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Dec 20;23(1):415. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02392-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39707467 Free PMC article.
-
Precision medicine using molecular-target drugs in psoriatic arthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2025 Jan 5;17:1759720X241311462. doi: 10.1177/1759720X241311462. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2025. PMID: 39776828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated clustering reveals CD4+ T cell subset imbalances in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 May 5;14:1094872. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1094872. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37215131 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

