Insulin Resistance Markers to Detect Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Male Hispanic Population
- PMID: 35966932
- PMCID: PMC9365587
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1782221
Insulin Resistance Markers to Detect Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Male Hispanic Population
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the leading causes of chronic liver disease and is closely associated with cardiometabolic disorders, being insulin resistance (IR) the common pathogenic mechanism. The triglycerides/glucose (TyG) index and triglycerides/HDL-c (TG/HDL) ratio are markers correlated with IR. We compared the capacity of these two indexes, alongside IR, to detect NAFLD.
Methods: In a cross-sectional cohort study, we examined 263 active military personnel from the Colombian Air Force, aged between 29 and 54 years. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical determinations (glycemia, lipid profile, and insulin) were obtained, and ultrasound studies were performed to evaluate the presence of NAFLD. HOMA-IR index was calculated as (fasting insulin (µIU/mL) × fasting glucose (mmol/L)/22.5), the TyG index as Ln (triglycerides (mg/dL) × fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2), and the TG/HDL ratio as (triglycerides (mg/dL)/HDL-c (mg/dL)).
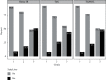
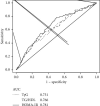
Results: NAFLD ultrasound criteria were met in 70 individuals (26.6%). Subjects with NAFLD had significantly higher values of HOMA-IR (2.55 ± 1.36 vs. 1.51 ± 0.91), TyG (9.17 ± 0.53 vs. 8.7 ± 0.51), and TG/HDL (6.6 ± 4.54 vs. 3.52 ± 2.32) compared to those without NAFLD (p < 0.001). A TyG cutoff point of 8.92 showed an AUC of 0.731, while cutoff points of 3.83 for TG/HDL and 1.68 for HOMA-IR showed an AUC of 0.766 and 0.781, respectively.
Conclusion: Our study shows that novel and lower-cost markers of IR are useful for detecting NALFD, with a performance comparable to the HOMA-IR index. These markers should be used as the first step when screening patients for NAFLD.
Copyright © 2022 Maritza Pérez-Mayorga et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

