Balance impairment in myotonic dystrophy type 1: Dynamic posturography suggests the coexistence of a proprioceptive and vestibular deficit
- PMID: 35967003
- PMCID: PMC9367988
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.925299
Balance impairment in myotonic dystrophy type 1: Dynamic posturography suggests the coexistence of a proprioceptive and vestibular deficit
Abstract
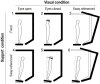
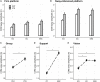
Falls are frequent in Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1), but the pathophysiology of the balance impairment needs further exploration in this disease. The current work aims to provide a richer understanding of DM1 imbalance. Standing balance in 16 patients and 40 controls was tested in two posturographic tests (EquiTest™). In the Sensory Organization Test (SOT), standstill balance was challenged by combining visual (eyes open vs. closed) and environmental conditions (fixed vs. sway-tuned platform and/or visual surround). In the "react" test, reflexes induced by sudden shifts in the support base were studied. Oscillations of the body centre of mass (COM) were measured. In the SOT, COM sway was larger in patients than controls in any condition, including firm support with eyes open (quiet standing). On sway-tuned support, COM oscillations when standing with closed eyes were larger in patients than controls even after taking into account the oscillations with eyes open. In the "react" paradigm, balance reflexes were delayed in patients. Results in both experimental paradigms (i.e., SOT and react test) are consistent with leg muscle weakness. This, however, is not a sufficient explanation. The SOT test highlighted that patients rely on vision more than controls to maintain static balance. Consistently enough, evidence is provided that an impairment of proprioceptive and vestibular systems contributes to falls in DM1. Rehabilitation programs targeted at reweighting sensory systems may be designed to improve safe mobility in DM1.
Keywords: balance; falls; myotonic dystrophy; neurological rehabilitation; posturography.
Copyright © 2022 Scarano, Sansone, Ferrari Aggradi, Carraro, Tesio, Amadei, Rota, Zanolini and Caronni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bachasson D., Moraux A., Ollivier G., Decostre V., Ledoux I., Gidaro T., et al. (2016). Relationship between muscle impairments, postural stability, and gait parameters assessed with lower-trunk accelerometry in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuromuscul. Disord. 26 428–435. 10.1016/j.nmd.2016.05.009 - DOI - PubMed

