Self-Assembling Oligo(2-oxazoline) Organogelators for the Encapsulation and Slow Release of Bioactive Volatiles
- PMID: 35967068
- PMCID: PMC9366986
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02905
Self-Assembling Oligo(2-oxazoline) Organogelators for the Encapsulation and Slow Release of Bioactive Volatiles
Abstract
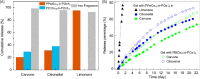
Herein, we report a class of distinctive supramolecular nanostructures in situ-generated from the cationic ring-opening polymerization of a particular 2-oxazoline monomer, i.e., 2-(N-tert-butyloxycarbonylaminomethyl)-2-oxazoline (Ox1). Driven by side-chain hydrogen bonding between neighboring molecules and van der Waals interactions, the growing oligomers of Ox1 precipitate in the form of macroscopic platelets when the degree of polymerization reaches 5-7. A similar self-assembly occurred in the block copolymerization of 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline (EtOx) or 2-pentyl-2-oxazoline (PeOx) and Ox1 as the second monomer. These polymeric aggregates were found to disassemble into rod-like nanoparticles under appropriate conditions, and to form stable organogels in some polar solvents like dimethylformamide as well as in natural liquid fragrances such as (R)-carvone, citronellal, and (R)-limonene. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that the morphology of their xerogels was solvent-dependent, mainly with a lamellar or fibrous structure. The rheology measurements confirmed the as-obtained organogels feature an obvious thixotropic character. The storage modulus was about 7-10 times higher than the loss modulus, indicating the physical crosslinking in the gel. The fragrance release profiles showed that the presented supramolecular gel system exhibits good sustained-release effect for the loaded bioactive volatiles.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Unravelling the Excellent Chemical Stability and Bioavailability of Solvent Responsive Curcumin-Loaded 2-Ethyl-2-oxazoline-grad-2-(4-dodecyloxyphenyl)-2-oxazoline Copolymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery.Biomacromolecules. 2018 Jul 9;19(7):2459-2471. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00057. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Biomacromolecules. 2018. PMID: 29634248
-
N-Alkylhydantoins as New Organogelators and Their Ability to Create Thixotropic Mixed Molecular Organogels.Gels. 2022 Oct 8;8(10):638. doi: 10.3390/gels8100638. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36286139 Free PMC article.
-
Supramolecular Glycolipid-Based Hydro-/Organogels with Enzymatic Bioactive Release Ability by Tuning the Chain Length and Headgroup Size.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022 Mar 14;8(3):1103-1114. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c01510. Epub 2022 Feb 23. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022. PMID: 35196000
-
Poly(2-oxazoline)s: a polymer class with numerous potential applications.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48(43):7978-94. doi: 10.1002/anie.200901607. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009. PMID: 19768817 Review.
-
Molecular Recognition Driven Bioinspired Directional Supramolecular Assembly of Amphiphilic (Macro)molecules and Proteins.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Jun 1;54(11):2670-2682. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00195. Epub 2021 May 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34014638 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlled Lactonization of o-Coumaric Esters Mediated by Supramolecular Gels.Gels. 2023 Apr 21;9(4):350. doi: 10.3390/gels9040350. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37102962 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

