The Role of Rituximab in Primary Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis of the Adult
- PMID: 35967114
- PMCID: PMC9366368
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.05.024
The Role of Rituximab in Primary Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis of the Adult
Abstract
Introduction: Primary focal segmental glomerular sclerosis (FSGS) is a rare, likely immune-mediated disease. Rituximab (RTX) may play a role in management, although data in adults are scanty.
Methods: We collected cases of RTX-treated primary FSGS within the Italian Society of Nephrology Immunopathology Working Group and explored response rate (24-hour proteinuria <3.5 g and <50% compared with baseline, stable estimated glomerular filtration rate).
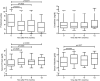
Results: A total of 31 patients were followed for at least 12 months; further follow-up (median 17 months, interquartile range [IQR] 15-33.5) was available for 11. At first RTX administration, median creatinine and 24-hour proteinuria were 1.17 mg/dl (IQR 0.83-1.62) and 5.2 g (IQR 3.3-8.81), respectively. Response rate at 3, 6, and 12 months was 39%, 52%, and 42%, respectively. In the first 12 months, creatinine level remained stable whereas proteinuria and serum albumin level improved, with an increase in the proportion of patients tapering other immunosuppressants. There were 6 patients who were retreated with RTX within 12 months, either for proteinuria increase or refractory disease; only the 2 responders to the first RTX course experienced a further response. At univariate analysis, 6-month response was more frequent in steroid-dependent patients (odds ratio [OR] 7.7 [95% CI 1.16-52.17]) and those with proteinuria <5 g/24 h (OR 8.25 [1.45-46.86]). During long-term follow-up, 4 of 5 responders at 12 months maintained a sustained response, either without further immunosuppression (2 of 4) or with pre-emptive RTX (2 of 4); 1 relapsed and responded to RTX retreatment.
Conclusion: RTX may be an option in primary FSGS, especially in steroid-dependent patients, with 24-hour proteinuria <5 g and previously responders to RTX. Optimal long-term management for responders is unclear, with some patients experiencing sustained remission and others requiring RTX retreatment, either preemptive or after rising proteinuria.
Keywords: focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; rituximab.
© 2022 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

