Early results of bare metal extension stent for thoracoabdominal aortic dissection
- PMID: 35967241
- PMCID: PMC9366534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjtc.2022.04.011
Early results of bare metal extension stent for thoracoabdominal aortic dissection
Abstract
Objectives: Debakey type I and IIIb aortic dissections are complicated by extension along the full length of the aorta. Over the long term, the thoracoabdominal aorta in these patients often continues to degenerate, requiring endovascular or open repair. The purpose of this investigation is to determine the early clinical outcome on aortic remodeling using a composite thoracic stent graft and thoracoabdominal bare metal extension stenting strategy.
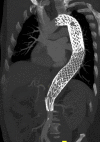
Methods: From April 2019 to April 2021, 73 patients with Debakey I/IIIb aortic dissection underwent endovascular stent graft repair of the descending thoracic aorta and repair of the thoracoabdominal aorta using bare metal extension stenting. Preoperative and follow-up surveillance computed tomography imaging scans were analyzed.
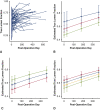
Results: Fifty-three (73%) patients had a Debakey I aortic dissection, and 50 (69%) patients underwent surgery during the chronic (time to surgery >30 days) dissection phase. Mortality at 30 days was 4% (3 hyperacute patients). Stroke occurred in 3 (4%), paraparesis in 2 (2.7%), and acute renal failure requiring dialysis occurred in 2 (2.7%) patients. On postoperative and follow-up computed tomography, there was a significant increase in false lumen thrombosis (P < .001). This coincided with a significant increase in true lumen fraction suggestive of positive aortic remodeling (P < .001) at the time of latest follow-up.
Conclusions: Altering the course of aortic remodeling, with placement of a dissection stent in the thoracoabdominal aorta simultaneous with descending thoracic aortic repair may promote true lumen re-expansion and false lumen thrombosis during acute and chronic dissection phases.
Keywords: CT, computed tomography; PETTICOAT; PETTICOAT, Provisional Extension to Induce Complete Attachment; TEVAR; TEVAR, thoracic endovascular aortic repair; aortic aneurysm; aortic dissection; endovascular.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures





References
-
- Arafat A., Roselli E.E., Idrees J.J., Feng K., Banaszak L., Eagleton M., et al. Stent grafting acute aortic dissection: comparison of Debakey extent IIIA versus IIIB. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102:1473–1481. - PubMed
-
- Fattori R., Tsai T.T., Myrmel T., Evangelista A., Cooper J.V., Trimarchi S., et al. Complicated acute type B dissection: is surgery still the best option?: a report from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;1:395–402. - PubMed
-
- Lombardi J.V., Hughes G.C., Appoo J.J., Bavaria J.E., Beck A.W., Cambria R.P., et al. Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS) and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) reporting standards for type B aortic dissections. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020;109:959–981. - PubMed
-
- Patterson B.O., Cobb R.J., Karthikesalingam A., Holt P.J., Hinchliffe R.J., Loftus I.M., et al. A systematic review of aortic remodeling after endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection: methods and outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:588–595. - PubMed
-
- Kang W.C., Greenberg R.K., Mastracci T.M., Eagleton M.J., Hernandez A.V., Pujara A.C., et al. Endovascular repair of complicated chronic distal aortic dissections: intermediate outcomes and complications. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:1074–1083. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

