A novel aGAPSS-based nomogram for the prediction of ischemic stroke in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome
- PMID: 35967319
- PMCID: PMC9372272
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930087
A novel aGAPSS-based nomogram for the prediction of ischemic stroke in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome
Abstract
Background: Ischemic stroke (IS) is the most common and life-threatening arterial manifestation of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). It is related to high mortality and severe permanent disability in survivors. Thus, it is essential to identify patients with APS at high risk of IS and adopt individual-level preventive measures. This study was conducted to identify risk factors for IS in patients with APS and to develop a nomogram specifically for IS prediction in these patients by combining the adjusted Global Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome Score (aGAPSS) with additional clinical and laboratory data.
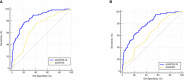
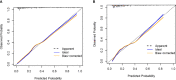
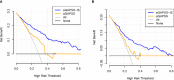
Methods: A total of 478 consecutive patients with APS were enrolled retrospectively. All patients were randomly assigned to the training and validation cohorts. Univariate and multivariate binary logistic analyses were conducted to identify predictors of IS in the training cohort. Then, a nomogram was developed based on these predictors. The predictive performance of the nomogram for the training and validation cohorts was evaluated by determining areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and creating calibration plots. A decision curve analysis (DCA) was conducted to compare the potential net benefits of the nomogram with those of the aGAPSS.
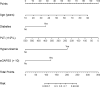
Results: During a mean follow-up period of 2.7 years, 26.9% (129/478) of the patients were diagnosed with IS. Binary logistic regression analysis revealed that five risk factors were independent clinical predictors of IS: age (P < 0.001), diabetes (P = 0.030), hyperuricemia (P < 0.001), the platelet count (P = 0.001), and the aGAPSS (P = 0.001). These predictors were incorporated into the nomogram, named the aGAPSS-IS. The nomogram showed satisfactory performance in the training [AUROC = 0.853 (95% CI, 0.802-0.896] and validation [AUROC = 0.793 (95% CI, 0.737-0.843)] cohorts. Calibration curves showed good concordance between observed and nomogram-predicted probability in the training and validation cohorts. The DCA confirmed that the aGAPSS-IS provided more net benefits than the aGAPSS in both cohorts.
Conclusion: Age, diabetes, hyperuricemia, the platelet count, and the aGAPSS were risk factors for IS in patients with APS. The aGAPSS-IS may be a good tool for IS risk stratification for patients with APS based on routinely available data.
Keywords: adjusted Global Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome Score; antiphospholipid syndrome; ischemic stroke; nomogram; risk stratification.
Copyright © 2022 Song, Fan, Jia, Li, Liu, Xu, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of the adjusted global antiphospholipid syndrome score in systemic lupus erythematosus patients in Argentina.Lupus. 2020 Dec;29(14):1866-1872. doi: 10.1177/0961203320960814. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Lupus. 2020. PMID: 33028177
-
The adjusted global antiphospholipid syndrome score (aGAPSS) and the risk of recurrent thrombosis: Results from the APS ACTION cohort.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Dec;49(3):464-468. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 May 2. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 31153708 Free PMC article.
-
The adjusted Global AntiphosPholipid Syndrome Score (aGAPSS) for risk stratification in young APS patients with acute myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Aug 1;240:72-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.02.155. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28385357
-
Clinical utility of the global anti-phospholipid syndrome score for risk stratification: a pooled analysis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018 Apr 1;57(4):661-665. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex466. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018. PMID: 29342292 Review.
-
Development of a nomogram for severe influenza in previously healthy children: a retrospective cohort study.J Int Med Res. 2023 Feb;51(2):3000605231153768. doi: 10.1177/03000605231153768. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 36802862 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperuricemia is a prognostic marker for antiphospholipid syndrome patients: a retrospective cohort study in China.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):2837-2847. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07480-2. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40493318
-
Antiphospholipid Antibodies Are Major Risk Factors for Non-Thrombotic Cardiac Complications in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 27;12(3):530. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030530. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540143 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of outcome in large vessel occlusion stroke patients with intravenous tirofiban treatment: a post hoc analysis of the RESCUE BT clinical trial.BMC Neurol. 2024 Jul 1;24(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03733-w. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38956505 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a nomogram model for 3-month prognosis in patients who had an acute ischaemic stroke after intravenous thrombolysis: a multifactor logistic regression model approach.BMJ Open. 2024 Jul 24;14(7):e079428. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-079428. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39053953 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors of first thrombosis in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome.Lupus Sci Med. 2024 Jan 3;11(1):e001044. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2023-001044. Lupus Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38176700 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

