Left ventricle- and skeletal muscle-derived fibroblasts exhibit a differential inflammatory and metabolic responsiveness to interleukin-6
- PMID: 35967380
- PMCID: PMC9366145
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947267
Left ventricle- and skeletal muscle-derived fibroblasts exhibit a differential inflammatory and metabolic responsiveness to interleukin-6
Abstract
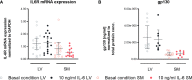
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is an important player in chronic inflammation associated with heart failure and tumor-induced cachexia. Fibroblasts are salient mediators of both inflammation and fibrosis. Whereas the general outcome of IL-6 on the heart's function and muscle wasting has been intensively studied, the influence of IL-6 on fibroblasts of the heart and skeletal muscle (SM) has not been analyzed so far. We illustrate that SM-derived fibroblasts exhibit higher basal mRNA expression of α-SMA, extracellular matrix molecules (collagen1a1/3a1/5a1), and chemokines (CCL2, CCL7, and CX3CL1) as compared to the left ventricle (LV)-derived fibroblasts. IL-6 drives the transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts as indicated by an increase in α-SMA expression and upregulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity in both LV- and SM-derived fibroblasts. IL-6 increases the release of CCL7 to CX3CL1 in the supernatant of SM-derived fibroblasts associated with the attraction of more pro(Ly6Chi) versus anti(Ly6Clo) inflammatory monocytes as compared to unstimulated fibroblasts. IL-6-stimulated LV-derived fibroblasts attract less Ly6Chi to Ly6Clo monocytes compared to IL-6-stimulated SM-derived fibroblasts. In addition, SM-derived fibroblasts have a higher mitochondrial energy turnover and lower glycolytic activity versus LV-derived fibroblasts under basal and IL-6 conditions. In conclusion, IL-6 modulates the inflammatory and metabolic phenotype of LV- and SM-originated fibroblasts.
Keywords: IL-6; NLRP3 inflammasome; fibroblasts; left ventricle; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2022 Matz, Pappritz, Springer and Van Linthout.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sex- and age-related differences in the inflammatory properties of cardiac fibroblasts: impact on the cardiosplenic axis and cardiac fibrosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Nov 20;10:1117419. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1117419. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 38054090 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia drives cardiac miRNAs and inflammation in the right and left ventricle.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Oct;97(10):1427-1438. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01817-6. Epub 2019 Jul 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31338525
-
Cardiac (myo)fibroblasts modulate the migration of monocyte subsets.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 3;8(1):5575. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23881-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29615815 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise as an anti-inflammatory therapy for cancer cachexia: a focus on interleukin-6 regulation.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):R296-R310. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00147.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31823669 Review.
-
TNF-α and cancer cachexia: Molecular insights and clinical implications.Life Sci. 2017 Feb 1;170:56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.11.033. Epub 2016 Dec 3. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27919820 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac fibroblasts and mechanosensation in heart development, health and disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023 May;20(5):309-324. doi: 10.1038/s41569-022-00799-2. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36376437 Review.
-
Update on preclinical models of cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction: Challenges and perspectives. A scientific statement of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC, the ESC Council of Cardio-Oncology, and the ESC Working Group on Cellular Biology of the Heart.Eur J Heart Fail. 2025 Jun;27(6):1028-1046. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.3636. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Eur J Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40069106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex- and age-related differences in the inflammatory properties of cardiac fibroblasts: impact on the cardiosplenic axis and cardiac fibrosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Nov 20;10:1117419. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1117419. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 38054090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evaluation, I.f.H.M.a. . Findings from the global burden of disease study 2017. Seattle, WA: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) (2018).
-
- Ridker PM, MacFadyen JG, Thuren T, Everett BM, Libby P, Glynn RJ, et al. . Effect of interleukin-1β inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (2017) 390(10105):1833–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32247-X - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

