Emerging concepts regarding pro- and anti tumor properties of B cells in tumor immunity
- PMID: 35967441
- PMCID: PMC9366002
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.881427
Emerging concepts regarding pro- and anti tumor properties of B cells in tumor immunity
Abstract
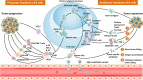
Controversial views regarding the roles of B cells in tumor immunity have existed for several decades. However, more recent studies have focused on its positive properties in antitumor immunity. Many studies have demonstrated a close association of the higher density of intratumoral B cells with favorable outcomes in cancer patients. B cells can interact with T cells as well as follicular dendritic cells within tertiary lymphoid structures, where they undergo a series of biological events, including clonal expansion, somatic hypermutation, class switching, and tumor-specific antibody production, which may trigger antitumor humoral responses. After activation, B cells can function as effector cells via direct tumor-killing, antigen-presenting activity, and production of tumor-specific antibodies. At the other extreme, B cells can obtain inhibitory functions by relevant stimuli, converting to regulatory B cells, which serve as an immunosuppressive arm to tumor immunity. Here we summarize our current understanding of the bipolar properties of B cells within the tumor immune microenvironment and propose potential B cell-based immunotherapeutic strategies, which may help promote cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: B-lymphocytes; humoral immunity; immunotherapy; prognosis; tertiary lymphoid structures; tumor microenvironment; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Copyright © 2022 Qin, Lu, Lyu, Chang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

