Cystatin C, renal resistance index, and kidney injury molecule-1 are potential early predictors of diabetic kidney disease in children with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 35967553
- PMCID: PMC9372344
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.962048
Cystatin C, renal resistance index, and kidney injury molecule-1 are potential early predictors of diabetic kidney disease in children with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the main cause of end-stage renal disease in patients with diabetes mellitus type I (DM-T1). Microalbuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) are standard predictors of DKD. However, these predictors have serious weaknesses. Our study aimed to analyze cystatin C, renal resistance index, and urinary kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) as predictors of DKD.
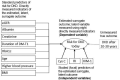
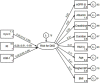
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study in 2019 on a consecutive sample of children and adolescents (10-18 years) diagnosed with DM-T1. The outcome was a risk for DKD estimated using standard predictors: age, urinary albumin, eGFR, serum creatinine, DM-T1 duration, HbA1c, blood pressure, and body mass index (BMI). We conducted the analysis using structural equation modeling.
Results: We enrolled 75 children, 36 girls and 39 boys with the median interquartile range (IQR) age of 14 (11-16) years and a median (IQR) duration of DM-T1 of 6 (4-9) years. The three focal predictors (cystatin C, resistance index, and urinary KIM-1) were significantly associated with the estimated risk for DKD. Raw path coefficients for cystatin C were 3.16 [95% CI 0.78; 5.53; p = 0.009, false discovery rate (FDR) < 5%], for renal resistance index were -8.14 (95% CI -15.36; -0.92; p = 0.027; FDR < 5%), and for urinary KIM-1 were 0.47 (95% CI 0.02; 0.93; p = 0.040; FDR < 5%).
Conclusion: Cystatin C, renal resistance index, and KIM-1 may be associated with the risk for DKD in children and adolescents diagnosed with DM-T1. We encourage further prospective cohort studies to test our results.
Keywords: adolescent; biomarkers; children; cystatin C; diabetes mellitus type 1; diabetic nephropathy; renal resistance index; urinary kidney injury molecule kIM-1.
Copyright © 2022 Trutin, Bajic, Turudic, Cvitkovic-Roic and Milosevic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dabelea D, Stafford JM, Mayer-Davis EJ, D’Agostino R, Dolan L, Imperatore G, et al. Association of type 1 diabetes vs type 2 diabetes diagnosed during childhood and adolescence with complications during teenage years and young adulthood. JAMA. (2017) 317:825. 10.1001/jama.2017.0686 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System (Usrds). Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. US Ren Data Syst 2019 Annu Data Rep. (2019). Available online at: https://usrds.org/media/2371/2019-executive-summary.pdf (accessed March 3, 2022).
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (Kdigo) Ckd-Mbd Update Work Group. KDIGO 2017 clinical practice guideline update for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl. (2017) 7:1–59. 10.1016/j.kisu.2017.04.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

