Stability of novel urinary biomarkers used for lupus nephritis
- PMID: 35967565
- PMCID: PMC9372620
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.974049
Stability of novel urinary biomarkers used for lupus nephritis
Abstract
Background: The Renal Activity Index for Lupus (RAIL) is a composite score of six urinary biomarkers (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), ceruloplasmin, adiponectin, and hemopexin) used to monitor lupus nephritis activity in children. We tested stability of RAIL biomarkers prior to meaningful clinical use.
Methods: Urine samples were tested by ELISA under shipping conditions, freeze/thaw, ambient and longer-term storage. Statistical analysis was performed via Deming Regression, Bland-Altman and Spearman Correlation Coefficient.
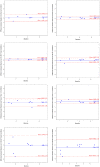
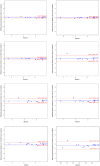
Results: Biomarker concentration were comparable to freshly collected urine following storage at -80 °C for up to 3 months, and at 4 or 25 °C up to 48 h followed by -80 °C. Neither shipping on dry or wet ice exposure nor addition of two freeze-thaw cycles led to loss of signal, with excellent Spearman Correlation coefficients under all conditions.
Conclusions: RAIL biomarkers are stable following short-term storage at clinically relevant conditions.
Keywords: SLE; biomarker; lupus nephritis; stability; urine.
Copyright © 2022 Cody, Rose, Huang, Qiu, Brunner and Devarajan.
Conflict of interest statement
Author PD is a co-inventor on submitted patents for the use of NGAL as a biomarker of kidney disease. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

