The value of interleukin-27 for differentiating tuberculous pleural effusion from Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonic effusion in children
- PMID: 35967581
- PMCID: PMC9367962
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.948862
The value of interleukin-27 for differentiating tuberculous pleural effusion from Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonic effusion in children
Abstract
Objectives: The early diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion (TPE) is challenging due to the difficulty of isolating Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and pleural biomarkers are an optional choice. Recent studies showed that interleukin-27 (IL-27) appears to be a new accurate biomarker for TPE in adults and no related studies were reported in children. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the potential value of IL-27 in pediatric tuberculous pleurisy by detecting its levels in pleural fluid and serum.
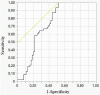
Methods: A total of 48 children with TPE and 64 children with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) pneumonic effusion (SMPPE) were enrolled in this study. IL-27 concentrations were measured in serum and pleural fluid. The diagnostic yield of IL-27 was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results: The level of p-IL-27 in TPE showed statistically no significant difference when compared with SMPPE (p > 0.05). However, pleural fluid IL-27 (p-IL-27) / serum IL-27 (s-IL-27) ratio in TPE were significantly much higher than those in SMPPE (p < 0.05). By the analysis of the ROC curves, the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of the p-IL-27/s-IL-27 ratio were 100% and 48.44%, respectively (cutoff value of 1.0280). The area under the ROC curve for p-IL-27/s-IL-27 was 0.7295.
Conclusion: Pleural fluid IL-27 alone was not accurate in distinguishing pediatric TPE from SMPPE, which was different from the diagnostic value of IL-27 in adult studies due to the different disease spectra between children and adults. Our results implied that the p-IL-27/s-IL-27 ratio had a potential value in distinguishing TPE from SMPPE. However, the specificity of IL-27 was relatively lower and it is necessary to find a more specific marker in tuberculous pleurisy of children.
Keywords: diagnosis; interleukin-27 (IL-27); mycoplasma; pleural effusion; tuberculous pleurisy.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Yang, Liu, Liu, Tang, Li, Cai and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020 Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources