Open controversies on the treatment of undescended testis: An update
- PMID: 35967583
- PMCID: PMC9363670
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.874995
Open controversies on the treatment of undescended testis: An update
Abstract
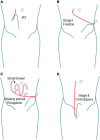
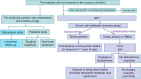
Cryptorchidism is a common congenital malformation in pediatric urology. Although there have been many studies on the etiology of the disease, it has not been fully clarified, and while its diagnostic and treatment models have gradually approached standardization and systematization, some controversies regarding treatment remain. Additionally, although ultrasound is a non-invasive examination without ionizing radiation, its role in the evaluation of cryptorchidism remains controversial. The main basis for treating cryptorchidism is orchidopexy, and the main view on treatment age is that treatment should be performed between 6 and 12 months after birth, but no more than 18 months after birth. The view on hormone therapy is still controversial because most scholars believe that early surgery is the key to treatment. There are many surgical treatment methods for cryptorchidism, including traditional open surgery and laparoscopic surgery, which provide satisfactory results. In conclusion, the treatment of undescended testis (UDT) had been largely standardized, apart from the treatment of high intra-abdominal testis (IAT), which remains a matter of debate.
Keywords: children; cryptorchidism; diagnosis; inguinal; surgery.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Xiu, Sui, Jin, Xu, Xia and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Secular trends in the incidence and timing of surgical intervention for congenital undescended testis and surgically treated hypospadias in Ontario, Canada between 1997 and 2007.J Pediatr Urol. 2018 Dec;14(6):552.e1-552.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Pediatr Urol. 2018. PMID: 30072120
-
Shortcomings in the management of undescended testis: guideline intention vs reality and the underlying causes - insights from the biggest German cohort.BJU Int. 2018 Oct;122(4):644-653. doi: 10.1111/bju.14171. Epub 2018 Mar 9. BJU Int. 2018. PMID: 29451709
-
Undescended testis: A roundtable discussion based on clinical scenarios - Part 1.J Pediatr Urol. 2024 Feb;20(1):95-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2023.09.023. Epub 2023 Oct 5. J Pediatr Urol. 2024. PMID: 37845102 Review.
-
Evaluation and management of the infant with cryptorchidism.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2015 Aug;27(4):520-4. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000237. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26087417 Review.
-
Management of undescended testis: a decision analysis.Med Decis Making. 2013 Oct;33(7):906-19. doi: 10.1177/0272989X13493145. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Med Decis Making. 2013. PMID: 23819984
Cited by
-
Retrocecal Ascending Appendix Attached to the Hepatic Flexure and Right Intra-abdominal Testis Identified During Open Appendicectomy: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Apr 2;16(4):e57484. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57484. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38577167 Free PMC article.
-
The role of E2F1 in promoting EIF4EBP1 transcription in cryptorchid mice: association with autophagy in germ cells.Front Genet. 2025 May 23;16:1536672. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1536672. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40486678 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic approach of inguinal hernia associated with adult cryptorchidism: case series and literature review.J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Apr 8;2024(4):rjae232. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjae232. eCollection 2024 Apr. J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38605699 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources