Development and initial validation of a clinical measure to assess symptoms of post-stroke depression in stroke patients at the rehabilitation stage
- PMID: 35967723
- PMCID: PMC9369669
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.928257
Development and initial validation of a clinical measure to assess symptoms of post-stroke depression in stroke patients at the rehabilitation stage
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Development and initial validation of a clinical measure to assess symptoms of post-stroke depression in stroke patients at the rehabilitation stage.Front Psychol. 2022 Nov 4;13:1076444. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1076444. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36405150 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The high incidence of post-stroke depression (PSD) during rehabilitation exerts a negative effect on the treatment and functional recovery of patients with stroke and increases the risk of mortality. It is necessary to screen PSD in the rehabilitation stage and thus provide effective intervention strategies. However, existing measurements used to assess PSD in the rehabilitation stage in patients with stroke lack specificity. This study aimed to develop a clinical measure to assess symptoms of PSD in the rehabilitation stage.
Methods: The research team created the initial items through a literature review and semi-structured interviews of patients with stroke. Then, the symptom-related items were estimated by three panels: healthcare professionals (N = 41), Delphi experts (N = 15), and patients with stroke in the rehabilitation stage (N = 30).
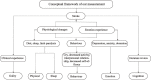
Results: The literature review and semi-structured interview produced 51 symptom-related items including six domains, and the items were reduced to 47 by the healthcare professionals. The symptom-related items were further reduced to 33 items by a two-round Delphi consultation. The initiative coefficients of the two Delphi rounds were 71.4 and 100%, the expert authority coefficients were both 0.85, Kendall's W were 0.152 and 0.408 (p < 0.01), and the coefficient of variation (CV) were 0.05-0.32 and 0.00-0.18, respectively. The item-level content validity index (I-CVI) was 0.53-1.00, the scale-level CVI/universal agreement (S-CVI/UA) was 0.26, and the S-CVI/average (S -CVI/Ave) was 0.85 for the first found Delphi consultation; the I-CVI was 0.67-1.00, the S-CVI/UA was 0.61, and the S-CVI/Ave was 0.97 for the second round Delphi consultation. All content validity indicators have been significantly improved compared with the first round. Using mean ≥ 4 and full score ≥ 0.5, combined with CV ≤ 0.16 as the item criteria, a clinical measure of PSD with 33 items and 6 dimensions (cognition, sleep, behavior, emotion, body, and guilt) was finally formed after two rounds. The patients with stroke made no further revisions after evaluation.
Conclusion: The research team developed a specific tool with good content validity to assess the symptoms of PSD in the rehabilitation stage.
Keywords: Delphi panel; content validity; instrument development; post-stroke depression; rehabilitation stage.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Liu, Zeng, Li, Wang, Ding, Guo, Lin and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploration of Establishing Evaluation Indicators for Hand Trauma Rehabilitation Nursing Based on Delphi Method.Ann Ital Chir. 2024;95(5):840-847. doi: 10.62713/aic.3627. Ann Ital Chir. 2024. PMID: 39467788
-
Measuring the determinants of implementation behavior in multiprofessional rehabilitation.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2023 Aug;59(4):488-501. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.23.07857-7. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2023. PMID: 37486174 Free PMC article.
-
Development and initial validation of a clinical measure to assess early symptoms of post-stroke depression in the acute stroke patient.J Clin Nurs. 2018 Feb;27(3-4):784-794. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14099. Epub 2017 Dec 6. J Clin Nurs. 2018. PMID: 28981176
-
Design and content validation of an instrument measuring user perception of the persuasive design principles in a breastfeeding mHealth app: A modified Delphi study.Int J Med Inform. 2022 Aug;164:104789. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2022.104789. Epub 2022 May 10. Int J Med Inform. 2022. PMID: 35597101 Review.
-
Identifying key elements to assess patient's acceptability of neurorehabilitation in stroke survivors - a Delphi method.Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Oct;44(21):6258-6266. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2021.1960438. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Disabil Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 34383623 Review.
Cited by
-
Research on patient-centered design for post-stroke depression patients based on SEM and comprehensive evaluation.Front Public Health. 2023 May 26;11:1120596. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1120596. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37304104 Free PMC article.
-
Factor structure and reliability of the symptom measurement of post-stroke depression in the rehabilitation stage.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 14;24(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05906-w. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38877421 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression in Patients with Ischaemic Stroke: A Cross-Sectional Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025 Apr 14;21:875-883. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S514184. eCollection 2025. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025. PMID: 40256205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida O. P., Almeida S. A. (1999). Short versions of the geriatric depression scale: a study of their validity for the diagnosis of a major depressive episode according to ICD-10 and DSM-IV. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 14 858–865. - PubMed
-
- Cannon W. (1929). Bodily Changes in Pain, Hunger, Fear and Rage. South. Med. J. 22:870. 10.1037/10013-000 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources