Pancreatic colonization of fungi in the development of severe acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 35967861
- PMCID: PMC9372468
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.940532
Pancreatic colonization of fungi in the development of severe acute pancreatitis
Abstract
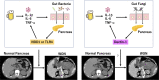
Acute pancreatitis is a common emergent disorder, a significant population of which develops the life-threatening condition, called severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). It is generally accepted that bacterial infection is associated with the development and persistence of SAP. In addition to bacterial infection, recent clinical studies disclosed a high incidence of fungal infection in patients with SAP. Moreover, SAP patients with fungal infection exhibit a higher mortality rate than those without infection. Although these clinical studies support pathogenic roles played by fungal infection in SAP, beneficial effects of prophylactic anti-fungal therapy on SAP have not been proved. Here we summarize recent clinical findings as to the relationship between fungal infection and the development of SAP. In addition, we discuss molecular mechanisms accounting for the development of SAP in the presence of fungal infection.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; cytokines; fungi; intestinal barrier; walled-off necrosis.
Copyright © 2022 Otsuka, Kamata, Minaga, Watanabe and Kudo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bhatt B., Cappell M. S. (1990). A peripancreatic abscess containing aspergillus in a patient with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 85 (9), 1200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

