The repositioned drugs disulfiram/diethyldithiocarbamate combined to benznidazole: Searching for Chagas disease selective therapy, preventing toxicity and drug resistance
- PMID: 35967878
- PMCID: PMC9372510
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.926699
The repositioned drugs disulfiram/diethyldithiocarbamate combined to benznidazole: Searching for Chagas disease selective therapy, preventing toxicity and drug resistance
Abstract
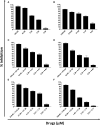
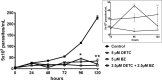
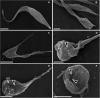
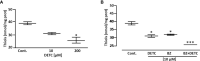
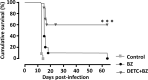
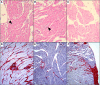
Chagas disease (CD) affects at least 6 million people in 21 South American countries besides several thousand in other nations all over the world. It is estimated that at least 14,000 people die every year of CD. Since vaccines are not available, chemotherapy remains of pivotal relevance. About 30% of the treated patients cannot complete the therapy because of severe adverse reactions. Thus, the search for novel drugs is required. Here we tested the benznidazole (BZ) combination with the repositioned drug disulfiram (DSF) and its derivative diethyldithiocarbamate (DETC) upon Trypanosoma cruzi in vitro and in vivo. DETC-BZ combination was synergistic diminishing epimastigote proliferation and enhancing selective indexes up to over 10-fold. DETC was effective upon amastigotes of the BZ- partially resistant Y and the BZ-resistant Colombiana strains. The combination reduced proliferation even using low concentrations (e.g., 2.5 µM). Scanning electron microscopy revealed membrane discontinuities and cell body volume reduction. Transmission electron microscopy revealed remarkable enlargement of endoplasmic reticulum cisternae besides, dilated mitochondria with decreased electron density and disorganized kinetoplast DNA. At advanced stages, the cytoplasm vacuolation apparently impaired compartmentation. The fluorescent probe H2-DCFDA indicates the increased production of reactive oxygen species associated with enhanced lipid peroxidation in parasites incubated with DETC. The biochemical measurement indicates the downmodulation of thiol expression. DETC inhibited superoxide dismutase activity on parasites was more pronounced than in infected mice. In order to approach the DETC effects on intracellular infection, peritoneal macrophages were infected with Colombiana trypomastigotes. DETC addition diminished parasite numbers and the DETC-BZ combination was effective, despite the low concentrations used. In the murine infection, the combination significantly enhanced animal survival, decreasing parasitemia over BZ. Histopathology revealed that low doses of BZ-treated animals presented myocardial amastigote, not observed in combination-treated animals. The picrosirius collagen staining showed reduced myocardial fibrosis. Aminotransferase de aspartate, Aminotransferase de alanine, Creatine kinase, and urea plasma levels demonstrated that the combination was non-toxic. As DSF and DETC can reduce the toxicity of other drugs and resistance phenotypes, such a combination may be safe and effective.
Keywords: Chagas disease; Diethyldithiocarbamate; Trypanosoma cruzi; chemotherapy; disulfiram; drug combination; repositioning.
Copyright © 2022 Almeida-Silva, Menezes, Fernandes, Almeida, Vasco-dos-Santos, Saraiva, Viçosa, Perez, Andrade, Suarez-Fontes and Vannier-Santos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






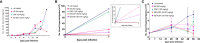

Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide donor trans-[RuCl([15]aneN)NO] as a possible therapeutic approach for Chagas' disease.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 May;160(2):270-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00576.x. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20128813 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo drug combination for the treatment of Trypanosoma cruzi infection: A multivariate approach.Exp Parasitol. 2018 Jun;189:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2018.04.016. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Exp Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29726395
-
Clomipramine and Benznidazole Act Synergistically and Ameliorate the Outcome of Experimental Chagas Disease.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 May 23;60(6):3700-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00404-16. Print 2016 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27067322 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro susceptibility of Trypanosoma cruzi discrete typing units (DTUs) to benznidazole: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Mar 22;15(3):e0009269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009269. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33750958 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanocidal drugs for late-stage, symptomatic Chagas disease (Trypanosoma cruzi infection).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 11;12(12):CD004102. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004102.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33305846 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Combination Therapy of Curcumin and Disulfiram Synergistically Inhibits the Growth of B16-F10 Melanoma Cells by Inducing Oxidative Stress.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 31;12(11):1600. doi: 10.3390/biom12111600. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358950 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfiram: Mechanisms, Applications, and Challenges.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;12(3):524. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030524. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug screening and development cascade for Chagas disease: an update of in vitro and in vivo experimental models.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024 Jul 1;119:e240057. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760240057. eCollection 2024. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024. PMID: 38958341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Recent Medicinal Applications of Rhenium(I) Tricarbonyl Complexes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 21;26(14):7005. doi: 10.3390/ijms26147005. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of diethyldithiocarbamate with copper ions and its liposomal formulation for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms.Biofilm. 2023 May 17;5:100130. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2023.100130. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biofilm. 2023. PMID: 37274173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrade S. G., Kloetzel J. K., Borges M. M., Ferrans V. J. (1994). Morphological aspects of the myocarditis and myositis in Calomys callosus experimentally infected with Trypanosoma cruzi: fibrogenesis and spontaneous regression of fibrosis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 89 (3), 379–393. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02761994000300017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ângelo de Souza L., Silva e Bastos M., de Melo Agripino J., Souza Onofre T., Apaza Calla L. F., Heimburg T., et al. . (2020). Histone deacetylases inhibitors as new potential drugs against Leishmania braziliensis, the main causative agent of new world tegumentary leishmaniasis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 180, 114191. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114191 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

