Time-Restricted Ketogenic Diet in Huntington's Disease: A Case Study
- PMID: 35967897
- PMCID: PMC9372583
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.931636
Time-Restricted Ketogenic Diet in Huntington's Disease: A Case Study
Abstract
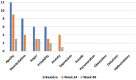
Huntington's disease (HD) is a progressive, fatal neurodegenerative disorder with limited treatment options. Substantial evidence implicates mitochondria dysfunction in brain and skeletal muscle in the pathogenesis of HD. Metabolic strategies, such as fasting and ketogenic diets, theoretically enhance brain and muscle metabolism and mitochondria function, which may improve the clinical symptoms of HD. We report the case of a 41-year-old man with progressive, deteriorating HD who pursued a time-restricted ketogenic diet (TRKD) for 48 weeks. Improvements were measured in his motor symptoms (52% improvement from baseline), activities of daily living (28% improvement), composite Unified HD Rating Scale (cUHDRS) score (20% improvement), HD-related behavior problems (apathy, disorientation, anger, and irritability improved by 50-100%), and mood-related quality of life (25% improvement). Cognition did not improve. Weight remained stable and there were no significant adverse effects. This case study is unique in that a patient with progressive, deteriorating HD was managed with a TRKD, with subsequent improvements in his motor symptoms, activities of daily living, cUHDRS score, most major HD-related behavior problems, and quality of life. Our patient remains dedicated to his TRKD, which continues to provide benefit for him and his family.
Keywords: Huntington's disease; energy metabolism; fasting; ketogenic diet; metabolic strategy; mitochondria dysfunction; neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2022 Phillips, McManus, Brinkhuis and Romero-Ferrando.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Time-restricted ketogenic diet in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a case study.Front Neurol. 2024 Jan 18;14:1329541. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1329541. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38304328 Free PMC article.
-
A digital motor score for sensitive detection of progression in Huntington's disease.Brain. 2025 Apr 11:awaf127. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf127. Online ahead of print. Brain. 2025. PMID: 40215265
-
Composite UHDRS Correlates With Progression of Imaging Biomarkers in Huntington's Disease.Mov Disord. 2021 May;36(5):1259-1264. doi: 10.1002/mds.28489. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Mov Disord. 2021. PMID: 33471951
-
Influence of dietary patterns in the pathophysiology of Huntington's Disease: A literature review.AIMS Neurosci. 2024 Apr 12;11(2):63-75. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2024005. eCollection 2024. AIMS Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38988882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Intake, Mediterranean Diet Adherence and Caloric Intake in Huntington's Disease: A Review.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 25;12(10):2946. doi: 10.3390/nu12102946. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32992896 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian Interventions in Preclinical Models of Huntington's Disease: A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):1777. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081777. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary fasting and time-restricted eating in Huntington's disease: therapeutic potential and underlying mechanisms.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Apr 2;13(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00406-z. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 38561866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Neuroprotection by Ketone Bodies and Ketogenic Diet in Cerebral Ischemia and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):124. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010124. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence-Based Review on Symptomatic Management of Huntington's Disease.J Mov Disord. 2024 Oct;17(4):369-386. doi: 10.14802/jmd.24140. Epub 2024 Aug 9. J Mov Disord. 2024. PMID: 39117301 Free PMC article.
-
The microbiota-gut-brain axis in Huntington's disease: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic targets.FEBS J. 2025 Mar;292(6):1282-1315. doi: 10.1111/febs.17102. Epub 2024 Mar 1. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 38426291 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

