Development of a human antibody that exhibits antagonistic activity toward CC chemokine receptor 7
- PMID: 35967907
- PMCID: PMC9372883
- DOI: 10.1093/abt/tbac016
Development of a human antibody that exhibits antagonistic activity toward CC chemokine receptor 7
Abstract
Background: CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) is a member of G-protein-coupled receptor family and mediates chemotactic migration of immune cells and different cancer cells induced via chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 (CCL19) or chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 (CCL21). Hence, the identification of blockade antibodies against CCR7 could lead to the development of therapeutics targeting metastatic cancer.
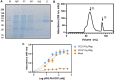
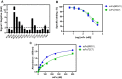
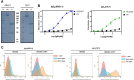
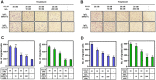
Methods: CCR7 was purified and stabilized in its active conformation, and antibodies specific to purified CCR7 were screened from the synthetic M13 phage library displaying humanized scFvs. The in vitro characterization of selected scFvs identified two scFvs that exhibited CCL19-competitive binding to CCR7. IgG4's harboring selected scFv sequences were characterized for binding activity in CCR7+ cells, inhibitory activity toward CCR7-dependent cAMP attenuation, and the CCL19 or CCL21-dependent migration of CCR7+ cells.
Results: Antibodies specifically binding to purified CCR7 and CCR7+ cells were isolated and characterized. Two antibodies, IgG4(6RG11) and IgG4(72C7), showed ligand-dependent competitive binding to CCR7 with KD values of 40 nM and 50 nM, respectively. Particularly, IgG4(6RG11) showed antagonistic activity against CCR7, whereas both antibodies significantly blocked the ligand-induced migration and invasion activity of CCR7+ cancer cells.
Conclusions: Two antibody clones were successfully identified from a synthetic scFv-displaying phage library using purified recombinant CCR7 as an antigen. Antibodies specifically bound to the surface of CCR7+ cells and blocked CCR7+ cell migration. Particularly, 6RG11 showed antagonist activity against CCR7-dependent cAMP attenuation.
Keywords: CC chemokine receptor 7; GPCR; antibody; metastasis; phage display.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Antibody Therapeutics. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Bryce, SA, Wilson, RAM, Tiplady, EMet al. . ACKR4 on stromal cells scavenges CCL19 to enable CCR7-dependent trafficking of APCs from inflamed skin to lymph nodes. J Immunol 2016; 196: 3341–53. - PubMed
-
- Förster, R, Davalos-Misslitz, AC, Rot, A. CCR7 and its ligands: balancing immunity and tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8: 362–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
