The molecular understanding of super-enhancer dysregulation in cancer
- PMID: 35967935
- PMCID: PMC9350580
- DOI: 10.18999/nagjms.84.2.216
The molecular understanding of super-enhancer dysregulation in cancer
Abstract
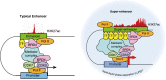
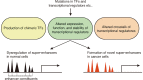
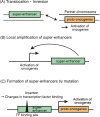
Abnormalities in the regulation of gene expression are associated with various pathological conditions. Among the distal regulatory elements in the genome, the activation of target genes by enhancers plays a central role in the formation of cell type-specific gene expression patterns. Super-enhancers are a subclass of enhancers that frequently contain multiple enhancer-like elements and are characterized by dense binding of master transcription factors and Mediator complexes and high signals of active histone marks. Super-enhancers have been studied in detail as important regulatory regions that control cell identity and contribute to the pathogenesis of diverse diseases. In cancer, super-enhancers have multifaceted roles by activating various oncogenes and other cancer-related genes and shaping characteristic gene expression patterns in cancer cells. Alterations in super-enhancer activities in cancer involve multiple mechanisms, including the dysregulation of transcription factors and the super-enhancer-associated genomic abnormalities. The study of super-enhancers could contribute to the identification of effective biomarkers and the development of cancer therapeutics targeting transcriptional addiction. In this review, we summarize the roles of super-enhancers in cancer biology, with a particular focus on hematopoietic malignancies, in which multiple super-enhancer alteration mechanisms have been reported.
Keywords: cancer therapy; genome; oncogene; super-enhancer; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
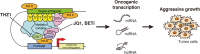
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
