Kinematic and mechanical modelling of a novel 4-DOF robotic needle guide for MRI-guided prostate intervention
- PMID: 35968253
- PMCID: PMC9365025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bea.2022.100036
Kinematic and mechanical modelling of a novel 4-DOF robotic needle guide for MRI-guided prostate intervention
Abstract
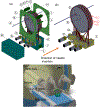
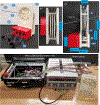
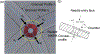
Traditionally ultrasound-guided biopsy has been used to diagnose prostate cancer despite of its poor soft tissue contrast and frequent false negative results. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has the advantage of excellent soft tissue contrast for guiding and monitoring prostate biopsy. However, its working area and access in the confined MRI bore space limit the use of interventional guide devices including robotic systems. To provide robotic precision, greater access, and compact design, we designed a novel robotic mechanism that can provide four degrees of freedom (DOF) manipulation in a compact form comparable to size of manual templates. To develop the mechanism, we established a mathematical model of inverse and forward kinematics and prototyped a proof-of-concept needle guide for MRI guided prostate biopsy. The mechanism was materialized using four discs that house small passive spherical joints that can be moved by rotating the discs consisting of grooved profile. With an initial needle insertion angle range of ±15°, we identified mathematical and kinematic parameters for the mechanism design and fabricated the first prototype that has dimension of 40 × 110 × 180 mm3. The prototype demonstrated that the unique robotic manipulation can physically be delivered and could provide precise needle guidance including angulated needle insertion with higher structural rigidity.
Keywords: Biopsy needle angulation; Kinematics; Parallel robot; Prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest There is no conflict of interest with our submitted manuscript titled “Kinematic and Mechanical modelling of a Novel 4-DOF Robotic Needle Guide for MRI-guided Prostate Intervention”.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vivo evaluation of angulated needle-guide template for MRI-guided transperineal prostate biopsy.Med Phys. 2021 May;48(5):2553-2565. doi: 10.1002/mp.14816. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33651407 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of an MRI-compatible pneumatic robot for angulated needle placement in transperineal prostate interventions.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2012 Nov;7(6):949-57. doi: 10.1007/s11548-012-0750-1. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2012. PMID: 22678723 Free PMC article.
-
Piezoelectrically Actuated Robotic System for MRI-Guided Prostate Percutaneous Therapy.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015 Aug;20(4):1920-1932. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2014.2359413. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015. PMID: 26412962 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic systems for percutaneous needle-guided interventions.Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2015 Feb;24(1):45-53. doi: 10.3109/13645706.2014.977299. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2015. PMID: 25421786 Review.
-
Review of Robotic Needle Guide Systems for Percutaneous Intervention.Ann Biomed Eng. 2019 Dec;47(12):2489-2513. doi: 10.1007/s10439-019-02319-9. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Ann Biomed Eng. 2019. PMID: 31372856 Review.
References
-
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2021: American Cancer Society; 2021. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
