Current Advances in Paper-Based Biosensor Technologies for Rapid COVID-19 Diagnosis
- PMID: 35968255
- PMCID: PMC9363872
- DOI: 10.1007/s13206-022-00078-9
Current Advances in Paper-Based Biosensor Technologies for Rapid COVID-19 Diagnosis
Abstract
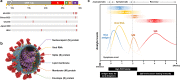
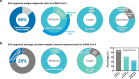
The global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has had significant economic and social impacts on billions of people worldwide since severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was first reported in Wuhan, China, in November 2019. Although polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based technology serves as a robust test to detect SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19, there is a high demand for cost-effective, rapid, comfortable, and accurate point-of-care diagnostic tests in medical facilities. This review introduces the SARS-CoV-2 viral structure and diagnostic biomarkers derived from viral components. A comprehensive introduction of a paper-based diagnostic platform, including detection mechanisms for various target biomarkers and a COVID-19 commercial kit is presented. Intrinsic limitations related to the poor performance of currently developed paper-based devices and unresolved issues are discussed. Furthermore, we provide insight into novel paper-based diagnostic platforms integrated with advanced technologies such as nanotechnology, aptamers, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-Cas. Finally, we discuss the prospects for the development of highly sensitive, accurate, cost-effective, and easy-to-use point-of-care COVID-19 diagnostic methods.
Keywords: COVID-19; Lateral flow assay (LFA); Paper-based biosensors; Point-of-care testing (POCT); SARS-CoV-2.
© The Korean BioChip Society 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Johns Hopkins University (JHU) and Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE), Coronavirus Resource Center., cited April 28, 2022. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
