Advancement of Organoid Technology in Regenerative Medicine
- PMID: 35968268
- PMCID: PMC9360642
- DOI: 10.1007/s40883-022-00271-0
Advancement of Organoid Technology in Regenerative Medicine
Abstract
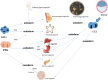
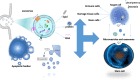
Purpose: Organoids are three-dimensional cultures of stem cells in an environment similar to the body's extracellular matrix. This is also a novel development in the realm of regenerative medicine. Stem cells can begin to develop into 3D structures by modifying signaling pathways. To form organoids, stem cells are transplanted into the extracellular matrix. Organoids have provided the required technologies to reproduce human tissues. As a result, it might be used in place of animal models in scientific study. The key goals of these investigations are research into viral and genetic illnesses, malignancies, and extracellular vesicles, pharmaceutical discovery, and organ transplantation. Organoids can help pave the road for precision medicine through genetic editing, pharmaceutical development, and cell therapy.
Methods: PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus were used to search for all relevant papers written in English (1907-2021). The study abstracts were scrutinized. Studies on the use of stem-cell-derived organoids in regenerative medicine, organoids as 3D culture models for EVs analysis, and organoids for precision medicine were included. Articles with other irrelevant aims, meetings, letters, commentaries, congress and conference abstracts, and articles with no available full texts were excluded.
Results: According to the included studies, organoids have various origins, types, and applications in regenerative and precision medicine, as well as an important role in studying extracellular vesicles.
Conclusion: Organoids are considered a bridge that connects preclinical studies to clinical ones. However, the lack of a standardized protocol and other barriers addressed in this review, hinder the vast use of this technology.
Lay summary: Organoids are 3D stem cell propagations in biological or synthetic scaffolds that mimic ECM to allow intercellular or matrix-cellular crosstalk. Because these structures are similar to organs in the body, they can be used as research models. Organoids are medicine's future hope for organ transplantation, tumor biobank formation, and the development of precision medicine. Organoid models can be used to study cell-to-cell interactions as well as effective factors like inflammation and aging. Bioengineering technologies are also used to define the size, shape, and composition of organoids before transforming them into precise structures. Finally, the importance of organoid applications in regenerative medicine has opened a new window for a better understanding of biological research, as discussed in this study.
Keywords: Organoid; Precision medicine; Regenerative medicine; Stem cells.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to The Regenerative Engineering Society 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-Cell and Spatial Analysis of Emergent Organoid Platforms.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2660:311-344. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3163-8_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37191807
-
Challenges for the Applications of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Liver Organoids.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 1;9:748576. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.748576. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34660606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Challenges Associated with the Use of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Organoids in Regenerative Medicine.Int J Stem Cells. 2021 Feb 28;14(1):9-20. doi: 10.15283/ijsc20140. Int J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33632980 Free PMC article.
-
Organoids: development and applications in disease models, drug discovery, precision medicine, and regenerative medicine.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 21;5(10):e735. doi: 10.1002/mco2.735. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39309690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma-derived extracellular matrix for xenofree and cost-effective organoid modeling for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2024 May 21;22(1):487. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05230-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38773585 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Human Brain Organoids in Migraine Research: Pathogenesis and Drug Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 4;24(4):3113. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043113. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834522 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Intestinal Stem Cells and Microbiota for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1470:115-128. doi: 10.1007/5584_2024_803. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38811486 Review.
-
Big data and its impact on the 3Rs: a home cage monitoring oriented review.Front Big Data. 2024 May 20;7:1390467. doi: 10.3389/fdata.2024.1390467. eCollection 2024. Front Big Data. 2024. PMID: 38831953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid-Mediated Extracellular Matrix Regulation: Implications for Precision Therapy.Biomedicines. 2025 May 23;13(6):1282. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061282. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic Scaffolds-A Novel Approach to Three Dimensional Cell Culture Techniques for Potential Implementation in Tissue Engineering.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Mar 16;14(6):531. doi: 10.3390/nano14060531. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38535679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leach TS, et al. et al. Chapter 83 - Tissue organoid models and applications. In: Lanza R, et al.et al., editors. Principles of Tissue Engineering. 5. Academic Press; 2020. pp. 1537–1549.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
