Dual role of ERK2/NF-κB signaling in TRAIL sensitivity
- PMID: 35968322
- PMCID: PMC9360224
Dual role of ERK2/NF-κB signaling in TRAIL sensitivity
Abstract
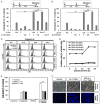
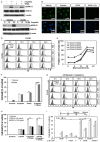
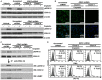
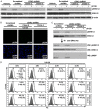
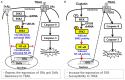
Targeting tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) signaling is a promising approach in cancer treatment. Although ERK and/or NF-κB signaling is involved in the expression of TRAIL receptors (TRAIL-R), the exact underlying mechanisms remain unknown. In this study, we evaluated the role of ERK2 and NF-κB in the cytotoxicity of TRAIL during cisplatin treatment. Cisplatin treatment of neuroepithelioma cells (SK-N-MC) significantly induced ERK2 activation and increased TRAIL cytotoxicity via the upregulation of death receptor 5 (DR5) expression. In partial ERK2 knockdown cell lines that maintained only basal levels of ERK2 activity, cisplatin treatment did not increase ERK2 activity or DR5 expression. These findings indicate that induced (rather than basal) ERK2 activity enhances TRAIL susceptibility via DR5 expression. In complete ERK2 knockdown cell lines with no basal ERK2 activity, DR4, DR5, and DcRs expression levels were increased, and additional treatment with cisplatin did not further increase TRAIL-R expression. Chemical inhibition of ERK2 also enhanced TRAIL cytotoxicity by upregulating DR4 and DR5 expression. These findings indicate that basal ERK2 activity suppresses TRAIL-R expression. Both basal and inducible ERK2 activities regulate TRAIL-R expression via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Overall, our findings suggest that the ERK2/NF-κB signaling pathway has a dual role in TRAIL susceptibility by differentially regulating TRAIL-R expression in the same cellular system.
Keywords: ERK2; NF-κB; TRAIL; cisplatin; death receptor.
AJCR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Wang S. The promise of cancer therapeutics targeting the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and TRAIL receptor pathway. Oncogene. 2008;27:6207–6215. - PubMed
-
- Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald ER 3rd, Jiang W, Meng R, Krantz ID, Kao G, Gan DD, Zhou JY, Muschel R, Hamilton SR, Spinner NB, Markowitz S, Wu G, el-Deiry WS. KILLER/DR5 is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated death receptor gene. Nat Genet. 1997;17:141–143. - PubMed
-
- Pan G, O’Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R, Ebner R, Ni J, Dixit VM. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science. 1997;276:111–113. - PubMed
-
- Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, Ashkenazi A. Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity. 2000;12:611–620. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
