SHUBHCHINTAK: An efficient remote health monitoring approach for elderly people
- PMID: 35968413
- PMCID: PMC9361235
- DOI: 10.1007/s11042-022-13539-y
SHUBHCHINTAK: An efficient remote health monitoring approach for elderly people
Abstract
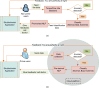
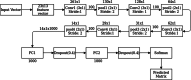
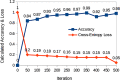
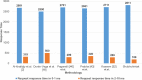
With the proliferation of IoT technology, it is anticipated that healthcare services, particularly for the elderly persons, will become a major thrust area of research in the coming days. Aim of this work is to design a fit-band containing multiple sensors to provide remote healthcare services for the elderly persons. An application has been designed to capture health data from the fit-band, pre-process the data and then send them to cloud for further analysis. A wireless Bluetooth enabled connection is proposed to establish communications between sensors and the application for data transmission. In the proposed application, there are three different front-end interfaces for three different users: system administrator, patient and doctor. The data collected from the patient's fit-band are sent to a cloud data storage, where the data will be analyzed to detect anomaly (e.g., heart attack, sleep apnea, etc.). A Convolution Neural Network (CNN) model is proposed for anomaly detection. For the classification of anomaly, a Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) model is proposed. In the presence of anomaly, the system immediately connects a doctor through a phone call. A prototype system termed as Shubhchintak has been developed in Android/IOS environment and tested with a number of users. The fit-band provides data tracking with an overall accuracy of 99%; the system provides a response with 3000 requests in less than 100 ms. Also, Shubhchintak provides a real-time feedback with an accuracy of 97%. Shubhchintak is also tested by patients and doctors of a nearby hospital. Shubhchintak is shown to be a simple to use, cost effective, comfortable, and efficient system compared to the existing state of the art solutions.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence approach to health data classification; Cloud-based application; Health anomaly for elderly people; Remote health monitoring; Wireless sensors.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestsThe authors declare no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures











Similar articles
-
A Novel Portable Real-Time Low-Cost Sleep Apnea Monitoring System based on the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Network.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022 Feb;60(2):619-632. doi: 10.1007/s11517-021-02492-x. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022. PMID: 35029814 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Intrusion Detection in Software-Defined Wireless Sensor Networks: Towards Secure IoT-Enabled Healthcare Systems.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 28;19(9):5367. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095367. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564763 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time artificial intelligence based health monitoring, diagnosing and environmental control system for COVID-19 patients.Math Biosci Eng. 2022 May 23;19(8):7586-7605. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022357. Math Biosci Eng. 2022. PMID: 35801437
-
Remote monitoring for long-term physical health conditions: an evidence and gap map.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023 Nov;11(22):1-74. doi: 10.3310/BVCF6192. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023. PMID: 38014553
-
Leveraging IoT-Aware Technologies and AI Techniques for Real-Time Critical Healthcare Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 10;22(19):7675. doi: 10.3390/s22197675. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drug discovery through Covid-19 genome sequencing with siamese graph convolutional neural network.Multimed Tools Appl. 2023 May 10:1-35. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-15270-8. Online ahead of print. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. PMID: 37362739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal S, Agrawal J. Survey on anomaly detection using data mining techniques. Procedia Computer Science. 2015;60:708–713. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.08.220. - DOI
-
- Al-Khafajiy M, Baker T, Chalmers C, et al. Remote health monitoring of the elderly through wearable sensors. Multimed Tools Appl. 2019;78:24681–24706. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-7134-7. - DOI
-
- American Diabetes Association (2019) 4. Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: standards of medical care in diabetes—2019. Diabetes care 42. Supplement 1:S34–S45 - PubMed
-
- Apple Inc. (2016) Introduction to HealthKit
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
