Incubation period of wild type of SARS-CoV-2 infections by age, gender, and epidemic periods
- PMID: 35968429
- PMCID: PMC9363879
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.905020
Incubation period of wild type of SARS-CoV-2 infections by age, gender, and epidemic periods
Abstract
Background: The incubation period of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is estimated to vary by demographic factors and the COVID-19 epidemic periods.
Objective: This study examined the incubation period of the wild type of SARS-CoV-2 infections by the different age groups, gender, and epidemic periods in South Korea.
Methods: We collected COVID-19 patient data from the Korean public health authorities and estimated the incubation period by fitting three different distributions, including log-normal, gamma, and Weibull distributions, after stratification by gender and age groups. To identify any temporal impact on the incubation period, we divided the study period into two different epidemic periods (Period-1: 19 January-19 April 2020 and Period-2: 20 April-16 October 2020), and assessed for any differences.
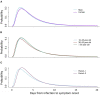
Results: We identified the log-normal as the best-fit model. The estimated median incubation period was 4.6 (95% CI: 3.9-4.9) days, and the 95th percentile was 11.7 (95% CI: 10.2-12.2) days. We found that the incubation period did not differ significantly between males and females (p = 0.42), age groups (p = 0.60), and the two different epidemic periods (p = 0.77).
Conclusions: The incubation period of wild type of SARS-CoV-2 infection during the COVID-19 pandemic 2020, in South Korea, does not likely differ by age group, gender and epidemic period.
Keywords: COVID-19; Korea; SARS-CoV-2; incubation period; log-normal distribution; quarantine.
Copyright © 2022 Achangwa, Park and Ryu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transmission dynamics and control of two epidemic waves of SARS-CoV-2 in South Korea.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 May 26;21(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06204-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34039296 Free PMC article.
-
Incubation period of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Busan, South Korea.J Infect Chemother. 2020 Sep;26(9):1011-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.06.018. Epub 2020 Jun 24. J Infect Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32631735 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on assessing early epidemiological parameters of COVID-19 epidemic in China].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 10;41(4):461-465. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200205-00069. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32113196 Chinese.
-
The Incubation Period Distribution of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Dec 16;73(12):2344-2352. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab501. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34117868
-
Incubation Period of COVID-19 Caused by Unique SARS-CoV-2 Strains: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Aug 1;5(8):e2228008. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.28008. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35994285 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessing changes in incubation period, serial interval, and generation time of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med. 2023 Sep 29;21(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03070-8. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37775772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- COVID Live Update: 201 005 476 Cases and 4 270 233 Deaths from the Coronavirus - Worldometer . Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed August 5, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

