Efficacy of Bevacizumab in High-Grade Meningiomas: A Retrospective Clinical Study
- PMID: 35968510
- PMCID: PMC9364983
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S368740
Efficacy of Bevacizumab in High-Grade Meningiomas: A Retrospective Clinical Study
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the role of bevacizumab (BV) in high-grade meningiomas (HGMs) by retrospective analysis.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 139 patients with HGMs. The chi-square test was used to compare progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) between patients who received BV and those who did not. According to whether they received BV treatment, we divided the patients into the BV group and non-BV group, and the effect of BV on PFS and OS was compared. In addition, we compared Karnofsky performance status (KPS) and steroid doses between the BV and non-BV groups.
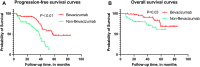
Results: There were statistically differences in PFS and OS between the BV and non-BV groups at 12 and 36 months after surgery (P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in PFS and OS between the two groups at 60 months postoperatively (P>0.05). Using survival curves drawn by the Kaplan Meier method, we found that the PFS and OS of the BV group were greater than those of the non-BV group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).
Conclusion: BV could improve PFS and OS at 12 and 36 months after surgery in patients with HGMs. In addition, BV was associated with lower preoperative steroid use.
Keywords: bevacizumab; meningiomas; overall survival; peritumoral brain edema; progression-free survival.
© 2022 Bai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dose and Efficacy of Bevacizumab in Recurrent High-Grade Gliomas: A Retrospective Study.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Nov 16;16:1617-1626. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S481289. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39575164 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-arterial delivery of bevacizumab after blood-brain barrier disruption for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma: progression-free survival and overall survival.World Neurosurg. 2012 Jan;77(1):130-4. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2011.05.056. Epub 2011 Nov 21. World Neurosurg. 2012. PMID: 22405392 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Karnofsky performance status predicts overall survival, cancer-specific survival, and progression-free survival following radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma.World J Urol. 2014 Apr;32(2):385-91. doi: 10.1007/s00345-013-1110-7. Epub 2013 Jun 12. World J Urol. 2014. PMID: 23756991
-
Cerebellar glioblastoma: a retrospective review of 21 patients at a single institution.J Neurooncol. 2011 Dec;105(3):555-62. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0617-2. Epub 2011 Jun 4. J Neurooncol. 2011. PMID: 21643841 Review.
-
Apatinib in recurrent anaplastic meningioma: a retrospective case series and systematic literature review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Jul 2;21(7):583-589. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1740053. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32212907 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bevacizumab for the Treatment of High-Grade Meningiomas: Is There New Evidence? [Letter].Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Oct 27;18:2453-2454. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S392309. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 36325433 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evolving treatment strategies in meningioma: from traditional approaches to emerging therapies.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Jul 16;87(8):5087-5097. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003556. eCollection 2025 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40787520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

