County-level variation in cardioprotective antihyperglycemic prescribing among medicare beneficiaries
- PMID: 35968531
- PMCID: PMC9364091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2022.100370
County-level variation in cardioprotective antihyperglycemic prescribing among medicare beneficiaries
Abstract
Background: Cardioprotective antihyperglycemic agents, SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1RA), improve outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes, but adoption has been limited. Differences across individuals have been noted but area-level variation is unknown.
Objectives: Given healthcare access and sociodemographic differences, we evaluated whether SGLT2i and GLP-1RA utilization varies across US counties.
Methods: We linked 2019 Medicare Part D national prescription data with county-level demographic measures from the Agency for Health Quality and Research. We compared the number of beneficiaries receiving prescriptions for any cardioprotective antihyperglycemic to the number receiving metformin prescriptions across US counties. In multivariable linear regression with SGLT2i-to-metformin and GLP1RA-to-metformin prescriptions as outcomes, we evaluated county factors associated with use of cardioprotective agents while adjusting for sociodemographic measures, region, and cardiometabolic risk factor prevalence.
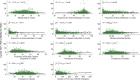
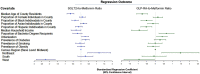
Results: In 3066 US counties, there were a median 2,416 (IQR, 1681-3190) metformin-receiving beneficiaries per 100,000 population. A median 6.2% of beneficiaries receiving metformin received SGLT2i therapy, varying across counties (IQR, 3.4%-9.2%). A median 9.4% (IQR, 5.0%-13.0%) of beneficiaries receiving metformin received GLP-1RA. In adjusted analyses, higher percentage of Black population was associated with lower use at the county level of people on SGLT2i or GLP-1RA relative to metformin (a SD higher proportion of Black individuals with 0.4% [95% CI, -0.6% to -0.1%] and 0.5% [-0.8% to -0.2%] lower SGLT2i and GLP-1RA prescribing relative to metformin, respectively; P < 0.01). A higher median age of county residents, rural location, and lower prevalence of diabetes were associated with lower SGLT2i prescribing. Similarly, more advanced age of county residents, rural location, proportion of Hispanic individuals, and household income and lower education levels were associated with lower GLP-1RA prescribing. Prescribing was higher in the Northeast and lower in the West as compared with the Midwest for both classes.
Conclusion: There was large variation by county in cardioprotective antihyperglycemic prescribing, with a pattern of lower use in Black-predominant and rural counties, highlighting the critical need to investigate equity in uptake of novel therapeutic agents.
Keywords: CI, confidence interval; GLP-1RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; Glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists; IQR, interquartile range; Medicare; PCP, primary care physicians; Prescription fill; SGLT2i, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors; Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Rohan Khera reports a relationship with Bristol-Myers Squibb that includes: funding grants. Rohan Khera reports a relationship with National Heart Lung and Blood Institute that includes: funding grants. Rohan Khera reports a relationship with Doris Duke Charitable Foundation that includes: funding grants. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with UnitedHealth Group that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with IBM Watson Health that includes: board membership. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Element Science that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Aetna Inc that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Facebook that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with F-Prime that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Siegfried & Jensen Law Firm that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Arnold & Porter Law Firm that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Martin Baughman Law Firm that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Beijing that includes: consulting or advisory. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services that includes: employment. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Medtronic Inc that includes: funding grants. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with US Food and Drug Administration that includes: funding grants. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Johnson & Johnson that includes: funding grants. Harlan Krumholz reports a relationship with Shenzhen Center for Health Information that includes: funding grants. Rohan Khera has patent #63/177,117 pending to Rohan Khera. Cofounder of HugoHealth and Refactor Health - HK; Founder of Evidence2Health - RK
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comparison of Diabetes Medications Used by Adults With Commercial Insurance vs Medicare Advantage, 2016 to 2019.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Feb 1;4(2):e2035792. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35792. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 33523188 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Prescribing Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors for Medicare Beneficiaries in the United States.Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2021 Dec;14(12):e008381. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.121.008381. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 34779654 Free PMC article.
-
Geographic variation in sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use in people with type 2 diabetes in New South Wales, Australia.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Jul;26(7):2787-2795. doi: 10.1111/dom.15597. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38618983
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists Versus Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.Cardiol Res. 2023 Feb;14(1):12-21. doi: 10.14740/cr1459. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Cardiol Res. 2023. PMID: 36896226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Oct;22(10):1857-1868. doi: 10.1111/dom.14108. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020. PMID: 32476254
Cited by
-
Social determinants of health and newer glucose-lowering drugs adoption among US Medicare beneficiaries with type 2 diabetes.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2024 Nov;30(11):1298-1307. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2024.30.11.1298. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39471265 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning in precision diabetes care and cardiovascular risk prediction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Sep 25;22(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01985-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37749579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geographic and Sociodemographic Factors and Receipt of Metabolic Disease Specialty Care.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 May 1;8(5):e2511559. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.11559. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 40392552 Free PMC article.
-
Comorbidities and neighborhood factors associated with prescription of sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among medically underserved populations.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2023 Jun;29(6):699-711. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2023.29.6.699. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37276038 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Patterns of Basal Insulin Use with Other Diabetes Medications Among People with Type 2 Diabetes Between 2014 and 2020.Diabetes Ther. 2023 Jul;14(7):1157-1174. doi: 10.1007/s13300-023-01414-4. Epub 2023 May 15. Diabetes Ther. 2023. PMID: 37184630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zelniker T.A., Wiviott S.D., Raz I., et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019;393:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Zelniker T.A., Wiviott S.D., Raz I., et al. Comparison of the effects of glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2019;139:2022–2031. - PubMed
-
- Marso S.P., Bain S.C., Consoli A., et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1834–1844. - PubMed
-
- Zinman B., Wanner C., Lachin J.M., et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–2128. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice C. 9 Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. 2021;45:S125. -S43. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

