Cefepime-Induced Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus in a Pediatric Patient with Normal Renal Function
- PMID: 35968536
- PMCID: PMC9364176
- DOI: 10.1177/2329048X221119575
Cefepime-Induced Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus in a Pediatric Patient with Normal Renal Function
Abstract
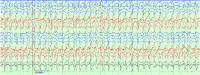
Introduction: Cefepime, a fourth-generation cephalosporin, is known to risk the induction of neurotoxic impairment from confusion to nonconvulsive status epilepticus (NCSE). Neurotoxic effects of cefepime are most commonly evident in the setting of impaired renal function in adults; however, are rarely present in those with normal renal excretion function or in the pediatric population. Case: We present a case of a 16-year-old female with a complicated past medical history but no accounts of impaired renal function yet, after starting cefepime, presented with encephalopathy, intermittent stimulus-induced posturing, and was found to have NCSE. Discontinuation of cefepime and administration of additional antiepileptics provided significant improvement in EEG and allowed the patient to return to baseline within two days. Conclusion: Cefepime-induced nonconvulsive status epilepticus should be considered in any patient with or without impaired renal function that shows acute changes in mental status, and/or reduced consciousness, after initiating cefepime treatment.
Keywords: EEG; cefepime; neurotoxicity; nonconvulsive status epilepticus; pediatric.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

