High HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol Increases Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertensive Patients
- PMID: 35968698
- PMCID: PMC9617028
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19912
High HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol Increases Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence suggests that elevated circulating levels of HDL-C (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) could be linked to an increased mortality risk. However, to the best of our knowledge, the relationship between HDL-C and specific cardiovascular events has never been investigated in patients with hypertension.
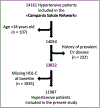
Methods: To fill this knowledge gap, we analyzed the relationship between HDL-C levels and cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients within the Campania Salute Network in Southern Italy.
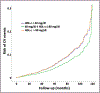
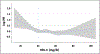
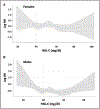
Results: We studied 11 987 patients with hypertension, who were followed for 25 534 person-years. Our population was divided in 3 groups according to the HDL-C plasma levels: HDL-C<40 mg/dL (low HDL-C); HDL-C between 40 and 80 mg/dL (medium HDL-C); and HDL-C>80 mg/dL (high HDL-C). At the follow-up analysis, adjusting for potential confounders, we observed a total of 245 cardiovascular events with a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular events in the low HDL-C group and in the high HDL-C arm compared with the medium HDL-C group. The spline analysis revealed a nonlinear U-shaped association between HDL-C levels and cardiovascular outcomes. Interestingly, the increased cardiovascular risk associated with high HDL-C was not confirmed in female patients.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that there is a U-shaped association between HDL-C and the risk of cardiovascular events in male patients with hypertension.
Keywords: cholesterol; dyslipidemias; heart disease risk factors; hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors; hypercholesterolemia; population; sex characteristics.
Figures
References
-
- Pekkanen J, Linn S, Heiss G, Suchindran CM, Leon A, Rifkind BM, Tyroler HA. Ten-year mortality from cardiovascular disease in relation to cholesterol level among men with and without preexisting cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1700–1707. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006143222403 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

