Accuracy of reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and loop-mediated isothermal amplification in diagnosing severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35968756
- PMCID: PMC9804528
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.28068
Accuracy of reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and loop-mediated isothermal amplification in diagnosing severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
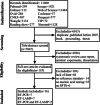
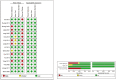
Nucleic acid molecular diagnostic technology plays an important role in the detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS). However, no relevant reports have been published on the accuracy of reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) in the diagnosis of SFTS. Thus, we conducted a meta-analysis and systematic review to evaluate the accuracy of the two methods. On June 19, 2022, we comprehensively searched the PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scoups, Ovid, Proquest, China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database, Wan Fang Data, Traditional Chinese Medicine Database (Sinomed), VIP Database, and Reading Showing Database for articles on nucleic acid diagnostic techniques, such as RT-PCR and RT-LAMP, used to diagnose SFTS. Statistical analysis was performed using STATA 14.0 and Meta-Disc 1.4. Sixteen articles involving 2942 clinical blood samples were included in the analysis. RT-PCR and RT-LAMP were used as index tests, whereas RT-PCR or other detection methods were used as reference standards. The pooled values for the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios of the RT-PCR test were 0.97 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.92-0.99), 1.00 (95% CI: 0.98-1.00), 483.87 (95% CI: 58.04-4033.76), and 0.03 (95% CI:0.01-0.08), respectively. Those for the RT-LAMP test were 0.95 (95% CI: 0.91-0.97), 0.99 (95% CI: 0.93-1.00), 111.18 (95% CI: 13.96-885.27), and 0.05 (95% CI: 0.03-0.09), respectively. Both RT-PCR and RT-LAMP have high diagnostic value in SFTS and can be applied in different scenarios for laboratory confirmation or on-site screening.
Keywords: RT-LAMP; RT-PCR; diagnose; meta-analysis; sever fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in clinical laboratories: A single-center study.J Med Virol. 2023 Dec;95(12):e29258. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29258. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 38054542
-
Development of an RT-LAMP Assay for the Rapid Detection of SFTS Virus.Viruses. 2021 Apr 16;13(4):693. doi: 10.3390/v13040693. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33923720 Free PMC article.
-
Simple and rapid detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in cats by reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay using a dried reagent.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 Mar 1;85(3):329-333. doi: 10.1292/jvms.22-0523. Epub 2023 Jan 18. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36653150 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse Transcriptase Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) for COVID-19 diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathog Glob Health. 2021 Jul;115(5):281-291. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2021.1933335. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Pathog Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34086539 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic efficiency of RT-LAMP integrated CRISPR-Cas technique for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathog Glob Health. 2022 Oct;116(7):410-420. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2022.2035625. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Pathog Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 35142264 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advancements in the Worldwide Detection of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection from 2009 to 2023.China CDC Wkly. 2023 Aug 4;5(31):687-693. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2023.132. China CDC Wkly. 2023. PMID: 37593140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu L, Chen W, Yang Y, Jiang Y. Molecular evolution of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukocytopenia virus (FTLSV) based on whole‐genome sequences. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;39:55‐63. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Li S, Yang L, Cao P, Lu J. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: A highly lethal bunyavirus. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2021;47(1):112‐25. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick‐borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(8):763‐72. - PubMed
-
- Gai ZT, Zhang Y, Liang MF, et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J Infect Dis. 2012;206(7):1095‐1102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

