Outcomes Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury Requiring Renal Replacement Therapy
- PMID: 35968778
- PMCID: PMC9683749
- DOI: 10.7812/TPP/21.197
Outcomes Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury Requiring Renal Replacement Therapy
Abstract
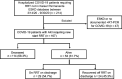
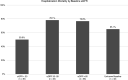
IntroductionAcute kidney injury (AKI) occurs in up to 10%-30% of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. AKI patients who require renal replacement therapy (RRT) often have concurrent respiratory failure and represent a high-mortality-risk population. The authors sought to describe outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with AKI requiring RRT and determine factors associated with poor outcomes. MethodsA retrospective cohort study of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with AKI requiring RRT during the period from March 14, 2020, to September 30, 2020, was performed at Kaiser Permanente Southern California. RRT was defined as conventional hemodialysis and/or continuous renal replacement therapy. The primary outcome was hospitalization mortality, and secondary outcomes were mechanical ventilation, vasopressor support, and dialysis dependence among discharged patients. Hospitalization mortality risk ratios were estimated up to 30 days from RRT initiation. ResultsA total of 167 hospitalized COVID-19 patients were identified with AKI requiring RRT. The study population had a mean age of 60.7 years and included 71.3% male patients and 60.5% Hispanic patients. Overall, 114 (68.3%) patients died during their hospitalization. Among patients with baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) values of ≥ 60, 30-59, and < 30 mL/min, the mortality rates were 76.8%, 78.1%, and 50.0%, respectively. Among the 53 patients who survived to hospital discharge, 29 (54.7%) continued to require RRT. Compared to patients with eGFR < 30 mL/min, the adjusted 30-day hospitalization mortality risk ratios (95% CI) were 1.38 (0.90-2.12) and 1.54 (1.06-2.25) for eGFR values of 30-59 and ≥ 60, respectively. ConclusionAmong a diverse cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with AKI requiring RRT, survival to discharge was low. Greater mortality was observed among patients with higher baseline kidney function. Most of the patients discharged alive continued to be dialysis-dependent.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute kidney injury; dialysis/renal replacement therapy; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of hospitalized patients with acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19 in Spain: renal replacement therapy and mortality. FRA-COVID SEN Registry Data.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024 Jul-Aug;44(4):527-539. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2023.03.017. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024. PMID: 39127584
-
AKI Treated with Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jan;32(1):161-176. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020060897. Epub 2020 Oct 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33067383 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Feb;77(2):204-215.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.09.002. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 32961245 Free PMC article.
-
Early versus late initiation of renal replacement therapy in patients with acute kidney injury-a systematic review & meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Feb 28;18(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0486-9. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28245793 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated versus standard initiation of renal replacement therapy for critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCT studies.Crit Care. 2021 Jan 5;25(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03434-z. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33402204 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Outcomes of Intermittent Hemodialysis versus Continuous Kidney Replacement Therapy in Hemodynamically Stable Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Prospective, Observational, Multicenter Study.Med Princ Pract. 2025;34(3):262-270. doi: 10.1159/000543882. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Med Princ Pract. 2025. PMID: 39904326 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Outcomes of 7620 Multiple Sclerosis Patients Admitted With COVID-19 in the United States.Neurohospitalist. 2024 Jul;14(3):237-241. doi: 10.1177/19418744241230728. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Neurohospitalist. 2024. PMID: 38895008 Free PMC article.
-
High-Flow Nasal Cannula Application After Extubation in Acute Respiratory Failure Patients.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 29;14(9):3087. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093087. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang X,Tian S,Guo H.Acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol.2021;90:107159.10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107159 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

