LIBRETTO-531: a phase III study of selpercatinib in multikinase inhibitor-naïve RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer
- PMID: 35969032
- PMCID: PMC10652291
- DOI: 10.2217/fon-2022-0657
LIBRETTO-531: a phase III study of selpercatinib in multikinase inhibitor-naïve RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer
Abstract
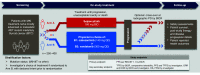
Selpercatinib is a first-in-class, highly selective and potent, central nervous system-active RET kinase inhibitor. In the phase I/II trial, selpercatinib demonstrated clinically meaningful antitumor activity with manageable toxicity in heavily pre-treated and treatment-naive patients with RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). LIBRETTO-531 (NCT04211337) is a multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled, phase III trial comparing selpercatinib to cabozantinib or vandetanib in patients with advanced/metastatic RET-mutant MTC. The primary objective is to compare progression-free survival (per RECIST 1.1) by blinded independent central review of patients with progressive, advanced, multikinase inhibitor-naive, RET-mutant MTC treated with selpercatinib versus cabozantinib or vandetanib. Key secondary objectives are to compare other efficacy outcomes (per RECIST 1.1) and tolerability of selpercatinib versus cabozantinib or vandetanib.
Keywords: RET alteration; RET kinase inhibitor; RET mutation; medullary thyroid cancer; phase III trial; selpercatinib; targeted therapy.
Plain language summary
Selpercatinib (also known by the brand name Retevmo®/Retsevmo®) is a new treatment available in multiple countries for people with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). Thyroid cancer starts in your thyroid gland and may spread or metastasize to other parts of the body, including lungs, bones, and occasionally the brain, which means the cancer is likely to be advanced. Advanced thyroid cancer can be driven by a gene in your body, one of which is RET. This is a summary of the LIBRETTO-531 study which compares selpercatinib, which is a strong and selective inhibitor of RET, with two approved drugs, cabozantinib and vandetanib. Patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who have not already received treatment with kinase inhibitors are being enrolled. This trial will evaluate how long people during and after treatment live with the disease without it getting worse. Selpercatinib may affect both healthy cells and tumor cells, which can result in side effects, which will also be evaluated in this study. This study is active and currently recruiting new patients. Clinical Trial Registration: NCT04211337 (ClinicalTrials.gov).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Durability of Response With Selpercatinib in Patients With RET-Activated Thyroid Cancer: Long-Term Safety and Efficacy From LIBRETTO-001.J Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 20;42(27):3187-3195. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.02503. Epub 2024 Aug 2. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39094065 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Selpercatinib in the treatment of thyroid cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Aug;21(20):2585-2592. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2531575. Epub 2025 Jul 10. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40638871 Review.
-
LIBRETTO-432, a phase III study of adjuvant selpercatinib or placebo in stage IB-IIIA RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2022 Sep;18(28):3133-3141. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0656. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35950566
-
Phase 3 Trial of Selpercatinib in Advanced RET-Mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2023 Nov 16;389(20):1851-1861. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309719. Epub 2023 Oct 21. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37870969 Clinical Trial.
-
Cabozantinib and vandetanib for unresectable locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer: a systematic review and economic model.Health Technol Assess. 2019 Feb;23(8):1-144. doi: 10.3310/hta23080. Health Technol Assess. 2019. PMID: 30821231 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular genetics, therapeutics and RET inhibitor resistance for medullary thyroid carcinoma and future perspectives.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 28;22(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01837-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39342195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 2024 revised clinical guidelines on the management of thyroid tumors by the Japan Association of Endocrine Surgery.Endocr J. 2025 May 7;72(5):545-635. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ24-0644. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Endocr J. 2025. PMID: 40058844 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis and Natural History of Medullary Thyroid Cancer: It is (Almost) All in the RET.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 5;15(19):4865. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194865. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Appropriate and mindful measurement of serum calcitonin in patients with thyroid nodules. A white paper.Endocrine. 2024 Jan;83(1):60-64. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03485-6. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 37589814 Free PMC article.
-
European Society of Endocrine Surgeons (ESES) consensus statement on advanced thyroid cancer: definitions and management.Br J Surg. 2024 Aug 2;111(8):znae199. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znae199. Br J Surg. 2024. PMID: 39158073 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolfe HJ, Melvin KE, Cervi-Skinner SJ et al. C-cell hyperplasia preceding medullary thyroid carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 289(9), 437–441 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Kouvaraki MA, Shapiro SE, Perrier ND et al. RET proto-oncogene: a review and update of genotype-phenotype correlations in hereditary medullary thyroid cancer and associated endocrine tumors. Thyroid 15(6), 531–544 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Accardo G, Conzo G, Esposito D et al. Genetics of medullary thyroid cancer: an overview. Int. J. Surg. 41(Suppl. 1), S2–S6 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Salvatore D, Santoro M, Schlumberger M. The importance of the RET gene in thyroid cancer and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 17(5), 296–306 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
