Lysocin E Targeting Menaquinone in the Membrane of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Is a Promising Lead Compound for Antituberculosis Drugs
- PMID: 35969044
- PMCID: PMC9487456
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00171-22
Lysocin E Targeting Menaquinone in the Membrane of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Is a Promising Lead Compound for Antituberculosis Drugs
Abstract
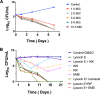
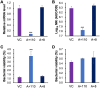
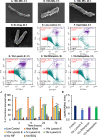
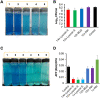
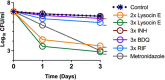
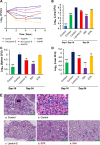
Tuberculosis remains a public health crisis and a health security threat. There is an urgent need to develop new antituberculosis drugs with novel modes of action to cure drug-resistant tuberculosis and shorten the chemotherapy period by sterilizing tissues infected with dormant bacteria. Lysocin E is an antibiotic that showed antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus by binding to its menaquinone (commonly known as vitamin K2). Unlike S. aureus, menaquinone is essential in both growing and dormant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This study aims to evaluate the antituberculosis activities of lysocin E and decipher its mode of action. We show that lysocin E has high in vitro activity against both drug-susceptible and drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. tuberculosis and dormant mycobacteria. Lysocin E is likely bound to menaquinone, causing M. tuberculosis membrane disruption, inhibition of oxygen consumption, and ATP synthesis. Thus, we have concluded that the high antituberculosis activity of lysocin E is attributable to its synergistic effects of membrane disruption and respiratory inhibition. The efficacy of lysocin E against intracellular M. tuberculosis in macrophages was lower than its potent activity against M. tuberculosis in culture medium, probably due to its low ability to penetrate cells, but its efficacy in mice was still superior to that of streptomycin. Our findings indicate that lysocin E is a promising lead compound for the development of a new tuberculosis drug that cures drug-resistant and latent tuberculosis in a shorter period.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; antituberculosis; lysocin E; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lysocin E is a new antibiotic that targets menaquinone in the bacterial membrane.Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Feb;11(2):127-33. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1710. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Nat Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25485686
-
A Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Demethylmenaquinone Methyltransferase MenG Is Bactericidal to Both Growing and Nutritionally Deprived Persister Cells.mBio. 2017 Feb 14;8(1):e02022-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02022-16. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28196957 Free PMC article.
-
[Development of next-generation antimicrobials with unique mechanisms of action].Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2024;79(3):275-281. doi: 10.3412/jsb.79.275. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2024. PMID: 39567002 Review. Japanese.
-
Serum apolipoprotein A-I potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of lysocin E against Staphylococcus aureus.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 4;12(1):6364. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26702-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34737305 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterial DNA Replication as a Target for Antituberculosis Drug Discovery.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017 Jun 16;17(19):2129-2142. doi: 10.2174/1568026617666170130114342. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28137234 Review.
Cited by
-
Silkworm model of bacterial infection facilitates the identification of lysocin E, a potent, ultra-rapid bactericidal antibiotic.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024 Aug;77(8):477-485. doi: 10.1038/s41429-024-00739-x. Epub 2024 May 21. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 38773231 Review.
-
Mycobacterial DNA-binding protein 1 is critical for BCG survival in stressful environments and simultaneously regulates gene expression.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 29;13(1):14157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40941-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37644087 Free PMC article.
-
Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance: Innovative Drugs in Antibacterial Research.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Mar 3;64(10):e202414325. doi: 10.1002/anie.202414325. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 39611429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tackling Nontuberculous Mycobacteria by Repurposable Drugs and Potential Leads from Natural Products.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(15):1291-1326. doi: 10.2174/0115680266276938240108060247. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38288807 Review.
-
Lead Informed Artificial Intelligence Mining of Antitubercular Host Defense Peptides.Biomacromolecules. 2025 May 12;26(5):3167-3179. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5c00244. Epub 2025 May 1. Biomacromolecules. 2025. PMID: 40310992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2021. Global tuberculosis report 2021. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021.
-
- Sukheja P, Kumar P, Mittal N, Li S, Singleton E, Russo R, Perryman AL, Shrestha R, Awasthi D, Husain S, Soteropoulos P, Brukh R, Connell N, Freundlich JS, Alland DA. 2017. A novel small-molecule inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis demethylmenaquinone methyltransferase MenG is bactericidal to both growing and nutritionally deprived persister cells. mBio 8:e02022-16. 10.1128/mBio.02022-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. 2020. Global tuberculosis report 2020. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

