Siderophores Produced by the Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium columnare Strain MS-FC-4 Are Not Essential for Its Virulence
- PMID: 35969053
- PMCID: PMC9469716
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.00948-22
Siderophores Produced by the Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium columnare Strain MS-FC-4 Are Not Essential for Its Virulence
Abstract
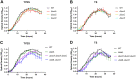
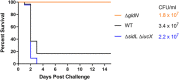
Flavobacterium columnare causes columnaris disease in wild and aquaculture-reared freshwater fish. F. columnare virulence mechanisms are not well understood, and current methods to control columnaris disease are inadequate. Iron acquisition from the host is important for the pathogenicity and virulence of many bacterial pathogens. F. columnare iron acquisition has not been studied in detail. We identified genes predicted to function in siderophore production for ferric iron uptake. Genes predicted to encode the proteins needed for siderophore synthesis, export, uptake, and regulation were deleted from F. columnare strain MS-FC-4. The mutants were examined for defects in siderophore production, for growth defects in iron-limited conditions, and for virulence against zebrafish and rainbow trout. Mutants lacking all siderophore activity were obtained. These mutants displayed growth defects when cultured under iron-limited conditions, but they retained virulence against zebrafish and rainbow trout similar to that exhibited by the wild type, indicating that the F. columnare MS-FC-4 siderophores are not required for virulence under the conditions tested. IMPORTANCE Columnaris disease, which is caused by Flavobacterium columnare, is a major problem for freshwater aquaculture. Little is known regarding F. columnare virulence factors, and control measures are limited. Iron acquisition mechanisms such as siderophores are important for virulence of other pathogens. We identified F. columnare siderophore biosynthesis, export, and uptake genes. Deletion of these genes eliminated siderophore production and resulted in growth defects under iron-limited conditions but did not alter virulence in rainbow trout or zebrafish. The results indicate that the F. columnare strain MS-FC-4 siderophores are not critical virulence factors under the conditions tested but may be important for survival under iron-limited conditions in natural aquatic environments or aquaculture systems.
Keywords: columnaris disease; fish pathogen; siderophore.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Flavobacterium columnare ferric iron uptake systems are required for virulence.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 17;12:1029833. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1029833. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36325469 Free PMC article.
-
Type IX Secretion System Effectors and Virulence of the Model Flavobacterium columnare Strain MS-FC-4.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Feb 8;88(3):e0170521. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01705-21. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34818105 Free PMC article.
-
The Type IX Secretion System Is Required for Virulence of the Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium columnare.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Nov 16;83(23):e01769-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01769-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28939608 Free PMC article.
-
Columnaris disease in fish: a review with emphasis on bacterium-host interactions.Vet Res. 2013 Apr 24;44(1):27. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-27. Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 23617544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron uptake mechanisms as key virulence factors in bacterial fish pathogens.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jul;129(1):104-115. doi: 10.1111/jam.14595. Epub 2020 Feb 12. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31994331 Review.
Cited by
-
Secreted peptidases contribute to virulence of fish pathogen Flavobacterium columnare.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Feb 3;13:1093393. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1093393. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36816589 Free PMC article.
-
Flavobacterium columnare ferric iron uptake systems are required for virulence.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 17;12:1029833. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1029833. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36325469 Free PMC article.
-
Gliding motility proteins GldJ and SprB contribute to Flavobacterium columnare virulence.J Bacteriol. 2024 Apr 18;206(4):e0006824. doi: 10.1128/jb.00068-24. Epub 2024 Mar 22. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38517170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davis HS. 1922. A new bacterial disease of freshwater fishes. Bull US Bureau Fish 38:261–280.
-
- Bullock GL, Hsu TC, Shotts EB. 1986. Columnaris disease of fishes. Fish Disease Leaflet 72; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Department of the Interior, Washington, DC.
-
- Zhang Y, Zhao L, Chen W, Huang Y, Yang L, Sarathbabu V, Wu Z, Li J, Nie P, Lin L. 2017. Complete genome sequence analysis of the fish pathogen Flavobacterium columnare provides insights into antibiotic resistance and pathogenicity related genes. Microb Pathog 111:203–211. 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.08.035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

