Invasive Group A Streptococcal Penicillin Binding Protein 2× Variants Associated with Reduced Susceptibility to β-Lactam Antibiotics in the United States, 2015-2021
- PMID: 35969070
- PMCID: PMC9487518
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00802-22
Invasive Group A Streptococcal Penicillin Binding Protein 2× Variants Associated with Reduced Susceptibility to β-Lactam Antibiotics in the United States, 2015-2021
Abstract
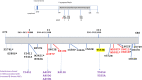
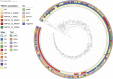
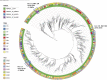
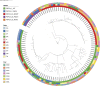
All known group A streptococci [GAS] are susceptible to β-lactam antibiotics. We recently identified an invasive GAS (iGAS) variant (emm43.4/PBP2x-T553K) with unusually high minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for ampicillin and amoxicillin, although clinically susceptible to β-lactams. We aimed to quantitate PBP2x variants, small changes in β-lactam MICs, and lineages within contemporary population-based iGAS. PBP2x substitutions were comprehensively identified among 13,727 iGAS recovered during 2015-2021, in the USA. Isolates were subjected to antimicrobial susceptibility testing employing low range agar diffusion and PBP2x variants were subjected to phylogenetic analyses. Fifty-five variants were defined based upon substitutions within an assigned PBP2x transpeptidase domain. Twenty-nine of these variants, representing 338/13,727 (2.5%) isolates and 16 emm types, exhibited slightly elevated β-lactam MICs, none of which were above clinical breakpoints. The emm43.4/PBP2x-T553K variant, comprised of two isolates, displayed the most significant phenotype (ampicillin MIC 0.25 μg/ml) and harbored missense mutations within 3 non-PBP genes with known involvement in antibiotic efflux, membrane insertion of PBP2x, and peptidoglycan remodeling. The proportion of all PBP2x variants with elevated MICs remained stable throughout 2015-2021 (<3.0%). The predominant lineage (emm4/PBP2x-M593T/ermT) was resistant to macrolides/lincosamides and comprised 129/340 (37.9%) of isolates with elevated β-lactam MICs. Continuing β-lactam selective pressure is likely to have selected PBP2x variants that had escaped scrutiny due to MICs that remain below clinical cutoffs. Higher MICs exhibited by emm43.4/PBP2x-T553K are probably rare due to the requirement of additional mutations. Although elevated β-lactam MICs remain uncommon, emm43.4/PBP2x-T553K and emm4/PBP2x-M593T/ermT lineages indicate that antibiotic stewardship and strain monitoring is necessary.
Keywords: PBP2x catalytic site; amino substituted β-lactams; clinical susceptibility; group A streptococcal lineages; penicillin binding protein 2×; transpeptidase domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Streptococcus pyogenes pbp2x Mutation Confers Reduced Susceptibility to β-Lactam Antibiotics.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jun 24;71(1):201-204. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1000. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31630171 Free PMC article.
-
Penicillin-Binding Protein Transpeptidase Signatures for Tracking and Predicting β-Lactam Resistance Levels in Streptococcus pneumoniae.mBio. 2016 Jun 14;7(3):e00756-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00756-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27302760 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of amino acid substitutions of penicillin-binding proteins 2B, 1A, 2X on minimal inhibitory concentration of beta-lactams against Streptococcus pneumoniae].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Jan;48(1):60-4. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20441706 Chinese.
-
A review of penicillin binding protein and group A Streptococcus with reduced-β-lactam susceptibility.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 31;13:1117160. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1117160. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37065204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Beta-lactam and macrolide resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae].Nihon Rinsho. 2001 Apr;59(4):681-6. Nihon Rinsho. 2001. PMID: 11304989 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
[Research progress on the mechanism of -lactam resistance in group A Streptococci in vivo].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jan 15;26(1):92-97. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2306157. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38269466 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Coordinated regulation of osmotic imbalance by c-di-AMP shapes ß-lactam tolerance in Group B Streptococcus.Microlife. 2024 Jun 12;5:uqae014. doi: 10.1093/femsml/uqae014. eCollection 2024. Microlife. 2024. PMID: 38993744 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis infection and its intersection with Streptococcus pyogenes.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Sep 12;37(3):e0017523. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00175-23. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38856686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Infection to Autoimmunity: S. pyogenes as a Model Pathogen.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 16;13(6):1398. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061398. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcus suis serotype 9 in Italy: genomic insights into high-risk clones with emerging resistance to penicillin.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024 Feb 1;79(2):403-411. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad395. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38153239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horn DL, Zabriskie JB, Austrian R, Cleary PP, Ferretti JJ, Fischetti VA, Gotschlich E, Kaplan EL, McCarty M, Opal SM, Roberts RB, Tomasz A, Wachtfogel Y. 1998. Why have group A streptococci remained susceptible to penicillin? Report on a symposium. Clin Infect Dis 26:1341–1345. 10.1086/516375. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

