Review: the role of GSDMD in sepsis
- PMID: 35969260
- PMCID: PMC9376580
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-022-01624-9
Review: the role of GSDMD in sepsis
Abstract
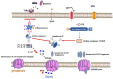
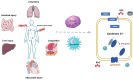
Purpose: Gasdermin D (GSDMD) is a cytoplasmic protein that is encoded by the gasdermin family GSDMD gene and is the ultimate executor of pyroptosis. Pyroptosis is a mode of lysis and inflammation that regulates cell death, ultimately leading to cell swelling and rupture. In sepsis, a dysregulated host response to infection frequently results in hyperinflammatory responses and immunosuppression, eventually leading to multiple organ dysfunction. Pyroptosis regulates innate immune defenses and plays an important role in the process of inflammatory cell death, and the absence of any link in the entire pathway from GSDMD to pyroptosis causes bacterial clearance to be hampered. Under normal conditions, the process of pyroptosis occurs much faster than apoptosis, and the threat to the body is also much greater.
Materials and methods: We conducted a systematic review of relevant reviews and experimental articles using the keywords sepsis, Gasdermin D, and Pyroptosis in the PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Web of Science databases.
Conclusion: Combined with the pathogenesis of sepsis, it is not difficult to find that pyroptosis plays a key role in bacterial inflammation and sepsis. Therefore, GSDMD inhibitors may be used as targeted drugs to treat sepsis by reducing the occurrence of pyroptosis. This review mainly discusses the key role of GSDMD in sepsis.
Keywords: Gasdermin D; Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome; Pyroptosis; Sepsis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GI-Y2, a novel gasdermin D inhibitor, attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by inhibiting gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis in macrophages.Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;182(15):3503-3521. doi: 10.1111/bph.70040. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Br J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40165368
-
GSDMD KNOCKOUT ALLEVIATES SEPSIS-ASSOCIATED SKELETAL MUSCLE ATROPHY BY INHIBITING IL18/AMPK SIGNALING.Shock. 2024 Oct 1;62(4):565-573. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002430. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Shock. 2024. PMID: 39227368
-
GSDMD and GSDME exhibit distinct roles in enteric coronavirus PDCoV-induced pyroptosis and inflammatory responses.J Virol. 2025 Jul 22;99(7):e0187624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01876-24. Epub 2025 Jun 12. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40503916 Free PMC article.
-
Automated monitoring compared to standard care for the early detection of sepsis in critically ill patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 25;6(6):CD012404. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012404.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29938790 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
Cited by
-
Identification and Analysis of PANoptosis-Related Genes in Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury by Bioinformatics and Experimental Verification.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Mar 28;17:1941-1956. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S452608. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38562657 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of pyroptosis and cytokine in the tumor microenvironment: from mechanisms to clinical implication.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 30;23(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02183-9. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39614288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The key players of inflammasomes and pyroptosis in sepsis-induced pathogenesis and organ dysfunction.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 19;16:1586364. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1586364. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40458798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phillyrin prevents sepsis-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting the NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis signaling pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Oct 10;57(3):447-462. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024161. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39394820 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Molecular Correlations of GSDMD with Pyroptosis inAlzheimer's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(14):2125-2139. doi: 10.2174/0113862073285497240226061936. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 39099451
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

