Angiotensin receptor blocker use is associated with upregulation of the memory-protective angiotensin type 4 receptor (AT4R) in the postmortem brains of individuals without cognitive impairment
- PMID: 35969296
- PMCID: PMC9886717
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-022-00639-8
Angiotensin receptor blocker use is associated with upregulation of the memory-protective angiotensin type 4 receptor (AT4R) in the postmortem brains of individuals without cognitive impairment
Abstract
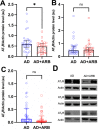
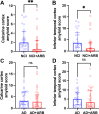
The reported primary dementia-protective benefits of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) blockers (ARB) are believed, at least in part, to arise from systemic effects on blood pressure. However, there is a specific and independently regulated brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Brain RAS acts mainly through three receptor subtypes; AT1R, AT2R, and AT4R. The AT1R promotes inflammation and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation. AT2R increases nitric oxide. AT4R is essential for dopamine and acetylcholine release. It is unknown whether ARB use is associated with changes in the brain RAS. Here, we compared the impact of treatment with ARB on not cognitively impaired individuals and individuals with Alzheimer's dementia using postmortem frontal-cortex samples of age- and sex-matched participants (70-90 years old, n = 30 in each group). We show that ARB use is associated with higher brain AT4R, lower oxidative stress, and amyloid-β burden in NCI participants. In AD, ARB use was associated with lower brain AT1R but had no impact on inflammation, oxidative stress, or amyloid-β burden. Our results may suggest a potential role for AT4R in the salutary effects for ARB on the brains of not cognitively impaired older adults.
Keywords: AT4R; Alzheimer’s disease; Angiotensin receptor blocker; Brain; Inflammation; Oxidative stress.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to American Aging Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Higher Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Levels and Activity in the Postmortem Brains of Older Persons with Alzheimer's Dementia.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022 Apr 1;77(4):664-672. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glab376. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34914835 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting brain Renin-Angiotensin System for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease: Past, present and future.Ageing Res Rev. 2022 May;77:101612. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101612. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Ageing Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 35346852 Review.
-
Brain angiotensin II and angiotensin IV receptors as potential Alzheimer's disease therapeutic targets.Geroscience. 2020 Oct;42(5):1237-1256. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00231-y. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Geroscience. 2020. PMID: 32700176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin IV Receptors Mediate the Cognitive and Cerebrovascular Benefits of Losartan in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Neurosci. 2017 May 31;37(22):5562-5573. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0329-17.2017. Epub 2017 May 5. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28476949 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between brain amyloid accumulation and the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers.Neurobiol Aging. 2021 Apr;100:22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.12.011. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Neurobiol Aging. 2021. PMID: 33461049
Cited by
-
The dopaminergic system and Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Sep 1;20(9):2495-2512. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00230. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39314145 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-beta metabolism in age-related neurocardiovascular diseases.Eur Heart J. 2025 Jan 16;46(3):250-272. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae655. Eur Heart J. 2025. PMID: 39527015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding Angiotensin Receptors: TOMAHAQ-Based Detection and Quantification of Angiotensin Type-1 and Type-2 Receptors.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Sep 19;12(18):e030791. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.030791. Epub 2023 Sep 8. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37681524 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Roles of Angiotensin A and Alamandine in Parkinson's Disease: A Therapeutic Perspective on Nonclassical RAS Pathways.Brain Behav. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70721. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70721. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40791030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preoperative continuation vs. discontinuation of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers on early cognitive function in elderly patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Mar 17;17:1542628. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1542628. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40166617 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

