Neuroprotective Potential of Intranasally Delivered Sulforaphane-Loaded Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Against Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity
- PMID: 35969308
- PMCID: PMC9515146
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-022-00555-x
Neuroprotective Potential of Intranasally Delivered Sulforaphane-Loaded Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Against Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity
Abstract
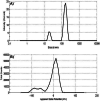
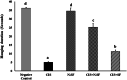
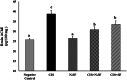
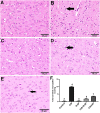
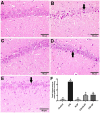
Cisplatin (CIS) is a platinum-based chemotherapeutic drug that is widely used to treat cancer. However, its therapeutic efficiency is limited due to its potential to provoke neurotoxicity. Sulforaphane (SF) is a natural phytochemical that demonstrated several protective activities. Iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4-NPs) could be used as drug carriers. This study aimed to explore the nanotoxic influence of SF-loaded within Fe3O4-NPs (N.SF), and to compare the neuroprotective potential of both N.SF and SF against CIS-induced neurotoxicity. N.SF or SF was administrated intranasally for 5 days before and 3 days after a single dose of CIS (12 mg/kg/week, i.p.) on the 6th day. Neuromuscular coordination was assessed using hanging wire and tail-flick tests. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activities and markers of oxidative stress were measured in the brain. In addition, the brain iron (Fe) content was estimated. CIS significantly induced a significant increase in AChE activities and lipid peroxides, and a significant decrement in glutathione (GSH) and nitric oxide (NO) contents. CIS elicited impaired neuromuscular function and thermal hyperalgesia. CIS-induced brains displayed a significant reduction in Fe content. Histopathological examination of different brain regions supported the biochemical and behavioral results. Contradict, treatment of CIS-rats with either N.SF or SF significantly decreased AChE activity, mitigated oxidative stress, and ameliorated the behavioral outcome. The histopathological features supported our results. Collectively, N.SF demonstrated superior neuroprotective activities on the behavioral, biochemical, and histopathological (striatum and cerebral cortex) aspects. N.SF could be regarded as a promising "pre-clinical" neuroprotective agent. Furthermore, this study confirmed the safe toxicological profile of Fe3O4-NPs.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Cisplatin; Intranasal; Iron oxide nanoparticles; Neurotoxicity; Sulforaphane.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Ali BH, Ramkumar A, Madanagopal TT, Waly MI, Tageldin M et al (2014) Motor and behavioral changes in mice with cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Physiological Res 63(1) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

