Therapeutic Usefulness of a Novel Calcium Channel Blocker Azelnidipine in the Treatment of Hypertension: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35969319
- PMCID: PMC9652186
- DOI: 10.1007/s40119-022-00276-4
Therapeutic Usefulness of a Novel Calcium Channel Blocker Azelnidipine in the Treatment of Hypertension: A Narrative Review
Abstract
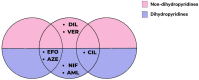
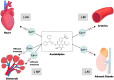
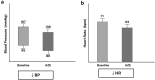
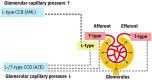
The prevalence of hypertension and comorbidities such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, and chronic kidney disease in India is alarmingly high. Amlodipine, an older-generation calcium channel blocker (CCB), is currently the gold standard for hypertension management in India. However, it has several disadvantages, including reflex tachycardia and pedal edema. Therefore, an effective antihypertensive agent that does not cause these adverse effects and provides end-organ protection is required for the holistic management of hypertension in the country. Azelnidipine is a new-generation CCB that has recently been approved for the treatment of hypertension in India. This review provides an overview of the utility of azelnidipine for hypertension control, including comparisons with traditional CCBs such as amlodipine. It discusses the key antihypertensive effects of azelnidipine as well as its advantages in the prevention of tachycardia and associated complications. In addition, this review highlights the extensive cardio- and renoprotective activities of azelnidipine, including its effects on systolic and diastolic function and urinary albumin excretion. Overall, this substantial body of evidence supports the use of azelnidipine for the treatment of hypertension, especially in India. It suggests that the adoption of azelnidipine as the new gold standard CCB could help India battle its hypertension epidemic.
Keywords: Antihypertensive agents; Azelnidipine; Calcium channel blockers; Chronic renal insufficiency; Diabetes mellitus; Hypertension; India; Metabolic syndrome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential effects of azelnidipine and amlodipine on sympathetic nerve activity in patients with primary hypertension.J Hypertens. 2014 Sep;32(9):1898-904. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000270. J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24979307 Clinical Trial.
-
Calcium channel blocker inhibition of AGE and RAGE axis limits renal injury in nondiabetic patients with stage I or II chronic kidney disease.Clin Cardiol. 2011 Jun;34(6):372-7. doi: 10.1002/clc.20885. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Clin Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21432860 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma renin activity and aldosterone concentration are not altered by the novel calcium channel antagonist, azelnidipine, in hypertensive patients.Intern Med. 2010;49(7):637-43. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2749. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Intern Med. 2010. PMID: 20371952
-
Azelnidipine.Drugs. 2003;63(23):2613-21; discussion 2623-4. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363230-00004. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 14636080 Review.
-
Calcium channel blockers for people with chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 1;10(10):CD011064. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011064.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33000470 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Antimicrobial Activity of Nisin Z Against S. aureus and Polyurea Pharmadendrimer PUREG4OEI48 Against P. aeruginosa from Diabetic Foot Infections.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Apr 28;14(5):444. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14050444. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426511 Free PMC article.
-
Azelnidipine and its role in decreasing urinary albumin creatinine ratio in people with type 2 diabetes and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024 Dec 16;24(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01538-9. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 39697863 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Azelnidipine as an Antihypertensive Compared to Amlodipine: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023 Sep;30(5):401-410. doi: 10.1007/s40292-023-00601-5. Epub 2023 Sep 28. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023. PMID: 37768510
-
Updates on Intrinsic Medicinal Chemistry of 1,4-dihydropyridines, Perspectives on Synthesis and Pharmacokinetics of Novel 1,4-dihydropyrimidines as Calcium Channel Blockers: Clinical Pharmacology.Curr Top Med Chem. 2025;25(11):1351-1376. doi: 10.2174/0115680266323908241114064318. Curr Top Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39754778 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Retrospective Study on the Mechanisms of Cyclic Mechanical Stretch-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Death Underlying Aortic Dissection and Potential Therapeutics for Preventing Acute Aortic Aneurysm and Associated Ruptures.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 22;25(5):2544. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052544. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2018;36:1953–2041. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Hypertension Fact Sheet. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension. Accessed 17 May 2022.
-
- Shah SN, Munjal YP, Kamath SA, et al. Indian guidelines on hypertension-IV (2019) J Hum Hypertens. 2020;34:745–758. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

