Microfluidic-Derived Detection of Protein-Facilitated Copper Flux Across Lipid Membranes
- PMID: 35969432
- PMCID: PMC9434548
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02081
Microfluidic-Derived Detection of Protein-Facilitated Copper Flux Across Lipid Membranes
Abstract
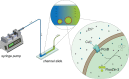
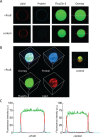
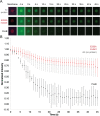
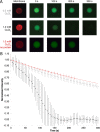
Measurement of protein-facilitated copper flux across biological membranes is a considerable challenge. Here, we demonstrate a straightforward microfluidic-derived approach for visualization and measurement of membranous Cu flux. Giant unilamellar vesicles, reconstituted with the membrane protein of interest, are prepared, surface-immobilized, and assessed using a novel quencher-sensor reporter system for detection of copper. With the aid of a syringe pump, the external buffer is exchanged, enabling consistent and precise exchange of solutes, without causing vesicle rupture or uneven local metal concentrations brought about by rapid mixing. This approach bypasses common issues encountered when studying heavy metal-ion flux, thereby providing a new platform for in vitro studies of metal homeostasis aspects that are critical for all cells, health, and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

