Nonlytic cellular release of hepatitis A virus requires dual capsid recruitment of the ESCRT-associated Bro1 domain proteins HD-PTP and ALIX
- PMID: 35969644
- PMCID: PMC9410543
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010543
Nonlytic cellular release of hepatitis A virus requires dual capsid recruitment of the ESCRT-associated Bro1 domain proteins HD-PTP and ALIX
Abstract
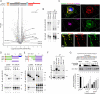
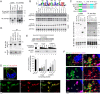
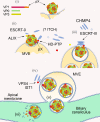
Although picornaviruses are conventionally considered 'nonenveloped', members of multiple picornaviral genera are released nonlytically from infected cells in extracellular vesicles. The mechanisms underlying this process are poorly understood. Here, we describe interactions of the hepatitis A virus (HAV) capsid with components of host endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) that play an essential role in release. We show release of quasi-enveloped virus (eHAV) in exosome-like vesicles requires a conserved export signal located within the 8 kDa C-terminal VP1 pX extension that functions in a manner analogous to late domains of canonical enveloped viruses. Fusing pX to a self-assembling engineered protein nanocage (EPN-pX) resulted in its ESCRT-dependent release in extracellular vesicles. Mutational analysis identified a 24 amino acid peptide sequence located within the center of pX that was both necessary and sufficient for nanocage release. Deleting a YxxL motif within this sequence ablated eHAV release, resulting in virus accumulating intracellularly. The pX export signal is conserved in non-human hepatoviruses from a wide range of mammalian species, and functional in pX sequences from bat hepatoviruses when fused to the nanocage protein, suggesting these viruses are released as quasi-enveloped virions. Quantitative proteomics identified multiple ESCRT-related proteins associating with EPN-pX, including ALG2-interacting protein X (ALIX), and its paralog, tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 23 (HD-PTP), a second Bro1 domain protein linked to sorting of ubiquitylated cargo into multivesicular endosomes. RNAi-mediated depletion of either Bro1 domain protein impeded eHAV release. Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy demonstrated colocalization of viral capsids with endogenous ALIX and HD-PTP. Co-immunoprecipitation assays using biotin-tagged peptides and recombinant proteins revealed pX interacts directly through the export signal with N-terminal Bro1 domains of both HD-PTP and ALIX. Our study identifies an exceptionally potent viral export signal mediating extracellular release of virus-sized protein assemblies and shows release requires non-redundant activities of both HD-PTP and ALIX.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- van der Grein SG, Defourny KAY, Rabouw HH, Galiveti CR, Langereis MA, Wauben MHM, et al. Picornavirus infection induces temporal release of multiple extracellular vesicle subsets that differ in molecular composition and infectious potential. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15(2):e1007594. Epub 2019/02/20. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007594 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

